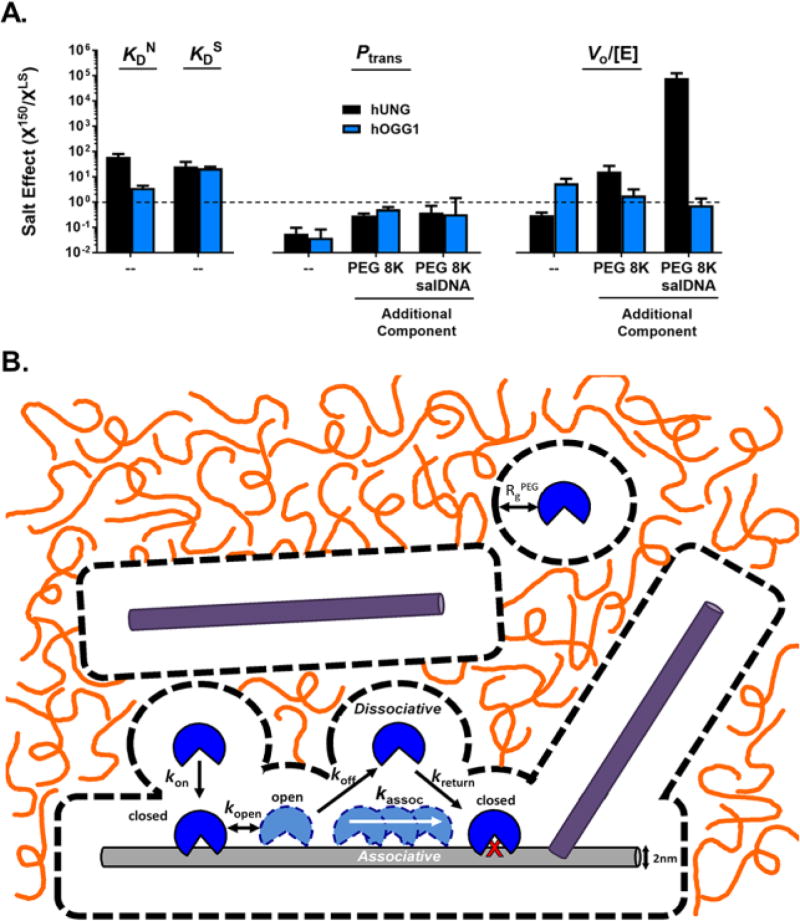
Figure 5.
Summary of the effects of salt, molecular crowding, and bulk DNA on each measured thermodynamic and kinetic parameter. (A) The salt effect (X150/XLS) is indicated for each solution condition we have explored. The salt effect is defined as the value of a given measurement (KD, Ptrans or V0/[E]) at 150 mM salt (X150) divided by the same measurement at low salt (XLS). This panel compares the salt effect in dilute buffered solution as compared to when 20% PEG8K, 1 mM bulk DNA, or both are present. Salt effects falling below the dashed line are reduced by high ionic strength and those above are enhanced. hUNG and hOGG1 respond differently to the introduction of salt with respect to non-specific DNA binding (KDN) and kinetic activity in the presence of crowder and salDNA. (B) General model for the effects of molecular crowders (orange lines) and bulk DNA (purple bars) on DNA translocation at a physiological salt concentration. The image is drawn to scale using a DNA duplex of with a 2 nm diameter as a scale reference. Dashed lines depict the depletion layer (RgPEG = 4.2 nm) where the PEG 8K polymer is excluded around the protein and DNA macromolecules60. Enzyme association with a substrate DNA chain (light gray) is limited by the bulk viscosity which hinders translational diffusion through the crowded solution, but is also is facilitated when the depletion layers of the enzyme and DNA overlap (see reference 9). Once this happens, the enzyme diffuses as if in a low viscosity environment. The depletion layer and polymer cage are very effective at enhancing DNA translocation by keeping dissociated enzyme molecules in the vicinity of the substrate DNA chain. Two effects of bulk DNA chains (dark gray) are also depicted. In the first scenario, the bulk DNA chain is enclosed in its own depletion layer and separated from the substrate DNA chain at a distance determined by the bulk DNA chain concentration. Such bulk DNA chains would be hindered from trapping translocating enzyme molecules compared to the absence of crowding. In the second scenario, the depletion layers of the bulk and substrate DNA have overlapped, which is facilitated by the reduced volume of complexation and shielding of the repulsive phosphate charge at high salt51, 53.