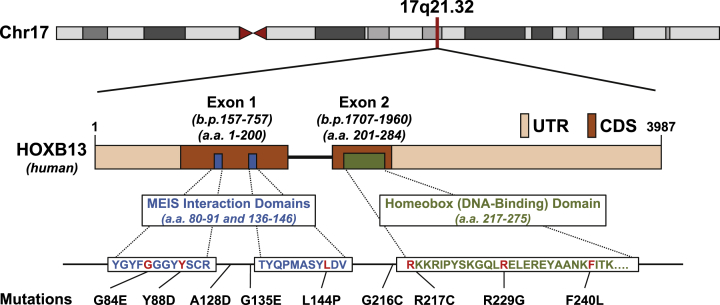
Fig. 2.
Genomic location, domains, and known mutations of human HOXB13. Since the original report of somatic HOXB13(G84E) mutations in a subset of familial cancer, more hereditary mutations conferring increased risk of prostate cancer have been identified (reference #2). The HOXB13 gene is located on human Chromosome 17q21.32 at the 5′ end of the 17q21-22 HOXB cluster, and consists of two exons and three known functional domains (accession number NC_000017/11 and ProtID Q92826). The HOXB13 transcript is 3987 base-pairs (b.p.) long, and Exons 1 and 2 are positioned at 157–757b.p. and 1707–1960b.p, respectively. The regions in beige indicates the untranslated regions (UTR), while the regions in brown indicate coding regions (CDR). The HOXB13 protein is 284 amino acids in length and contains two MEIS-interacting domains (amino acids 80–91 and 136–146) and a single DNA-binding homeobox domain (amino acids 217–275). The two Meis-interaction domains were functionally defined by Williams et al (reference #78 and 79), and the homeodomain was functionally defined in Zeltzer et al (reference #80). Clusters of mutations can be seen within or nearby the two MEIS-interacting domains and the homeodomain.