Figure 3.
The ribo-interactome consists of diverse functional groups.
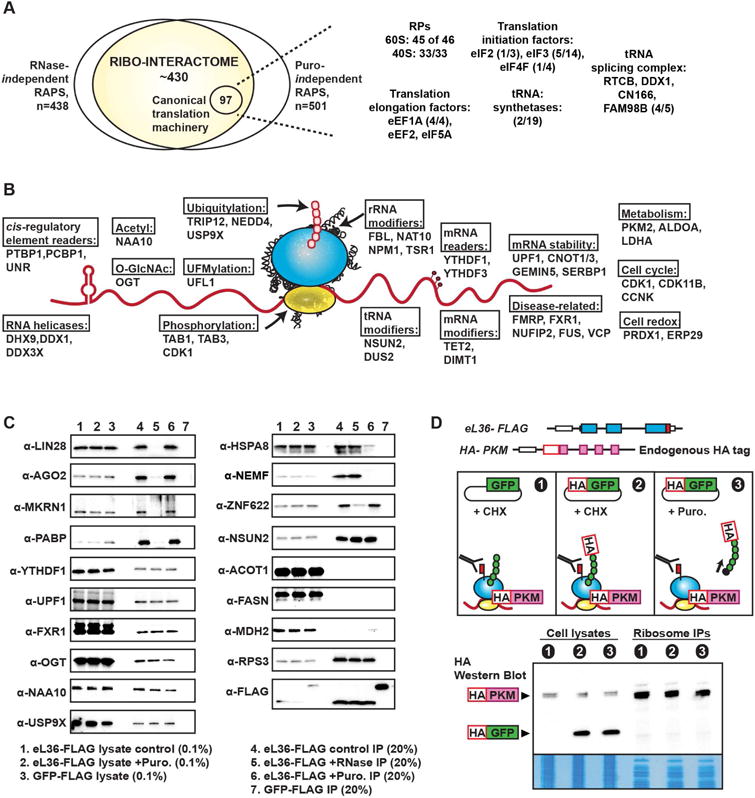
A, The ribo-interactome is defined as the intersection of RNase-independent and puromycin-independent interactions. The number of identified proteins related to canonical translation machinery in the MS experiments is presented along with the known number of factors in each class.
B, The ribosome as a hub for interactions with a multitude of proteins with diverse functions. Representative examples of direct ribosome interactors found in each functional group are presented. In the schematic, the pink circles represent the nascent peptides; red circles on the mRNA represent mRNA modifications.
C, Validation of representative examples from ribo-interactome. Western blots of the interactors from control, RNase-treated, and puromcyin-treated ribosome IP samples, along with the cytoplasmic lysates which are used as input control for these IPs.
D, PKM is endogenously tagged with HA within eL36-FLAG ES cells. Untagged GFP and HA-tagged GFP are further transfected into these cells. GFP does not interact with ribosomes, and is used as a negative control for possible ribosome interactions. GFP nascent chains are depicted by green circles. Western blots of the cell lysates and ribosome IPs are shown alongside Coomassie stained fractions. 0.01% of cytoplasmic lysates are used as input and 20% of the IPs are run in the western blot.
