Figure 1. cAMP is downstream the effect of Cl− on capacitation-associated increase activation of cAMP/PKA pathway.
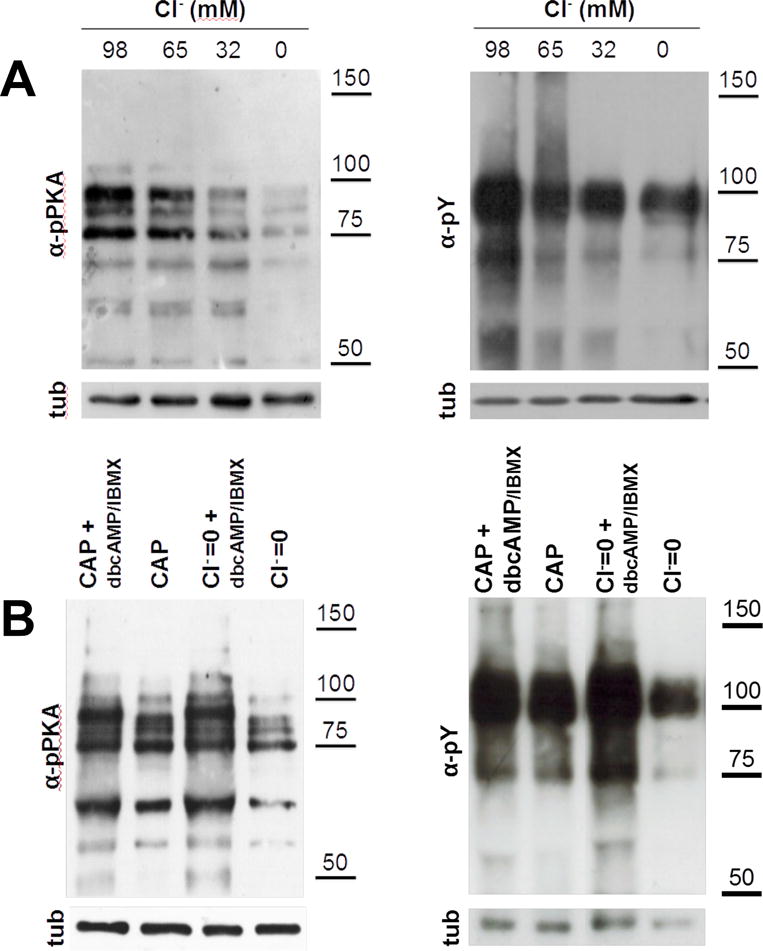
(A) As Cl− is one of the major anions transported by CFTR, sperm incubated in capacitating media for 1 (for pPKA) or 3 hours (for pY) with different Cl− concentrations (replaced by gluconate) to evaluate the effect of Cl− on the activation of cAMP/PKA pathway. Complete medium contains 98 mM of Cl−. Aliquots from each condition were processed for Western blotting with anti-pPKA antibodies (upper panel) and then membranes were reblotted with an anti-β-tubulin antibody for loading control (lower panel). The increase in the pY and pPKA is dependent on Cl− concentration and cAMP is downstream of the effect of Cl−. (B) Human sperm were incubated for 1 (for pPKA) or 3 hours (for pY) in media in the presence (CAP) or absence of Cl− (Cl−=0), IBMX (0.2 mM), and dbcAMP (1 mM). cAMP agonists rescued the inhibition of pY by the absence of Cl−. This experiment was repeated at least 4 times with similar results. For statistical analysis see Suppl. Fig. 2
