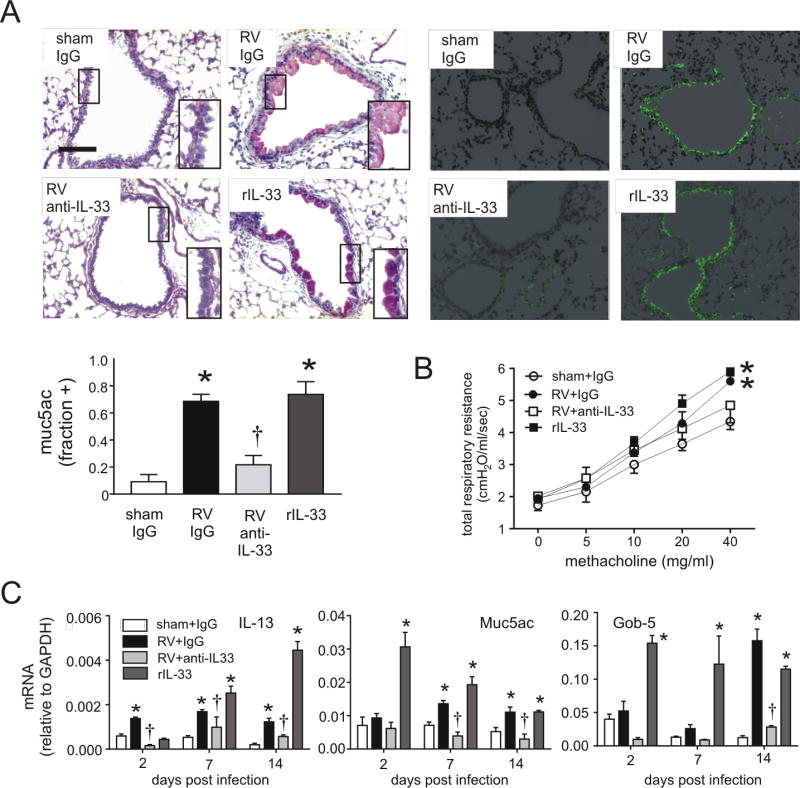
FIG 2.
Mucous metaplasia and lung mRNA expression in anti-IL-33- and rIL-33 treated mice. Six-day-old BALB/c mice were inoculated with sham, RV or rIL-33. Anti-IL-33 was given 1 hour after infection to selected RV-treated mice. A, Mucous metaplasia was assessed by periodic acid-Schiff-staining and Muc5ac immunofluorescence. Lung sections prepared 3 weeks after treatment of six day-old mice with sham + IgG, RV + IgG, RV + anti-IL-33 or rIL-33. (Bar = 50 µM.) Muc5ac was quantified as the fraction of epithelium positively stained, as measured by NIH ImageJ software (N=3, mean±SEM, *different from sham + IgG, p<0.05; different from RV + IgG, †p<0.05, one-way ANOVA). B, Airways hyperresponsiveness of 4 week-old baby mice, 21 days after sham infection, RV infection, RV + anti-IL33 or recombinant (r) IL-33 (n=4, *different from sham, p<0.05, two-way ANOVA). C, Whole lung gene expression of the mucus-related genes Muc5ac, Gob5 and IL-13 was measured with quantitative PCR. (N=3–5, mean±SEM, *different from sham, p<0.05; †different from RV + IgG, p<0.05, one-way ANOVA).