Figure 5. EphA2 deletion reduces advanced atherosclerotic progression.
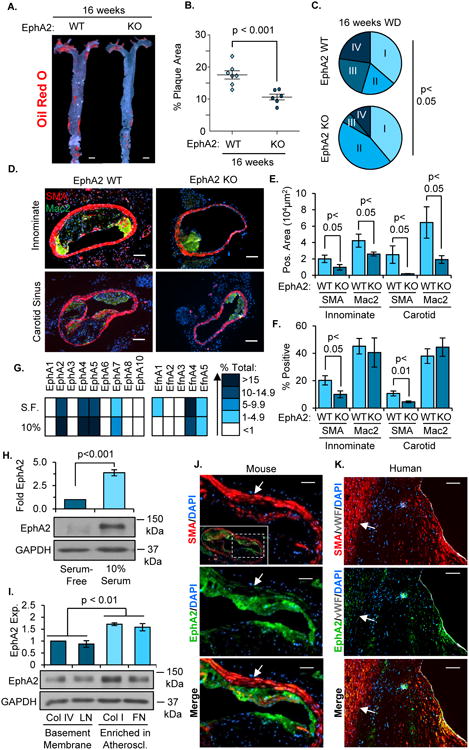
A, B) EphA2 WT and EphA2 KO mice were fed Western diet for 16 weeks, and atherosclerosis in the aortas was visualized by Oil Red O staining. n = 6-7. Scale bar = 1 mm. C) Atherosclerotic plaques from innominate arteries and carotid sinuses were graded for plaque scores based on a modified Stary scoring system. n = 22 plaques from 8 WT mice, 18 plaques from 6 KO mice. D-F) Atherosclerotic plaque composition was assessed by immunohistochemistry for macrophages (Mac2, green) and smooth muscle cells (SMA, red). Total macrophage and smooth muscle area were analyzed, and percent of the plaque area staining positive for SMA or Mac2 was calculated. Scale bar = 100 μm, n = 6-8. G/H) Human coronary artery smooth muscle cells (hCoASMCs) from 4 separate donors were either serum-starved or treated with 10% complete media for 3 days. G) mRNA was isolated and the expression of EphA and ephrinA family genes was quantified by qRT-PCR and normalized to GAPDH. Representative expression of each gene was determined and a heat map generated. H) EphA2 protein expression was determined by Western blot and normalized to GAPDH, n = 4. I) hCoASMCs were plated onto tissue culture dishes coated with collagen I (40 μg/mL), collagen IV (20 μg/mL), fibronectin (10 μg/mL), or laminin (20 μg/mL) and cultured for 3 days in serum-free conditions. EphA2 protein expression was assessed by Western blotting and normalized to GAPDH. n = 5. J/K) Smooth muscle EphA2 expression in atherosclerotic plaques was assessed by immunohistochemistry. Plaques from (J) the carotid artery of Apoe-/- mice fed Western diet for 16 weeks or (K) grade V human atherosclerotic lesions from coronary arteries were stained for EphA2 (green) and smooth muscle cells (SMA, red). White arrows indicate medial smooth muscle cells. Scale bar = 100 μm, n = 4-5. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, Statistical comparisons were made using Student's T-test (B, E, F, H), One-way ANOVA (I) with Bonferroni post-test, or Chi Squared test (C) comparing early stage (I and II) and advanced stage (III and IV) plaques.
