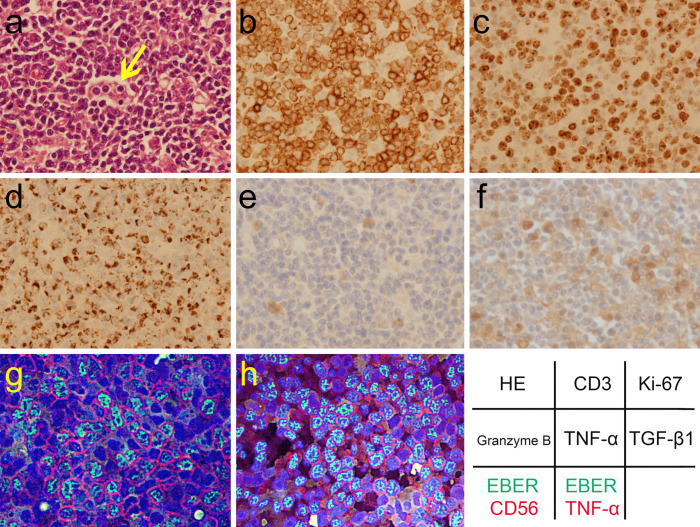
Figure 1.
The pathology of the NK-cell neoplasm with lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome from a resected lymph node. There are an increased number of atypical lymphoid cells with hemophagocytosis (arrow) on Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE) staining (a, ×40 of objective lens magnification). Immunohistochemical assay showed the immunophenotypes of the neoplasm: CD3+(b, ×40), CD4+, CD8−, CD20−, CD30+, and CD56+. The Ki-67 index was >90% (c, ×40). The neoplastic cells contained granzyme B (d, ×40). Immunohistochemical analysis of the stored biopsy samples also revealed expression of TNF-α+ (e, ×40) and TGF-β1+ (f, ×40), using TNFα (52B83) antibody (1:100 dilution; sc-52746; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, USA), and TGFβ1 (V) antibody (1:200 dilution; sc-146; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), respectively (13, 14). Hybrid fluorescence imaging of immunostaining and Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA (EBER)in situ hybridization precisely confirmed the immunophenotypes: green indicates EBER; red indicates CD56 (g, ×60) and TNF-α (1: 100 dilution; sc-52746; h, ×60) in each image; blue indicates DAPI-stained DNA. The component fluorescence images were taken with a fluorescence microscope BZ-8100 (Keyence, Osaka, Japan) by the second author.