Figure 2.
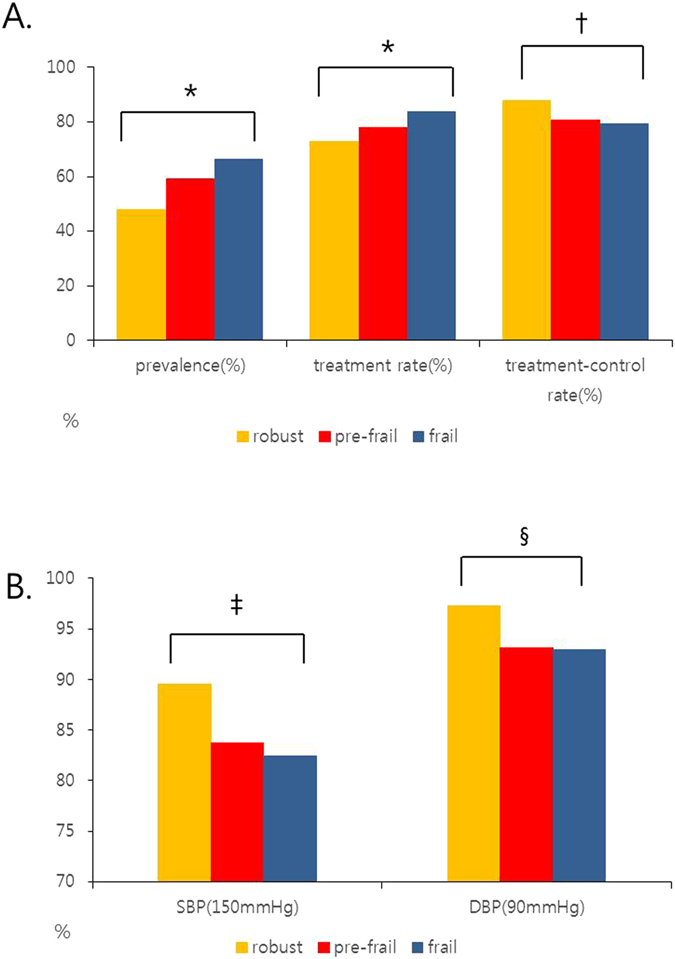
(A) Comparison of HTN prevalence and treatment, and control rate according to frailty status. (*P value < 0.001, † P value = 0.005). HTN prevalence was higher in frail elderly than pre-frail or robust elderly. (P < 0.001) In hypertensive patients, frail elderly are more likely to be treated than pre-frail or robust elderly (P < 0.001). In treated patients, the proportion of patients whose blood pressure was controlled under 150/90 mmHg was significantly lower in frail elderly (P = 0.005). (B) Comparison of SBP and DBP control rate in treated patients according to frailty status. (‡ P value = 0.020, § P value = 0.032). SBP: systolic blood pressure, DBP: diastolic blood pressure. In treated patients, the proportion of patients whose systolic blood pressure was controlled under 150 mmHg was significantly lower in frail elderly (P = 0.020), and the proportion of patients whose diastolic blood pressure was controlled under 90 mmHg was also lower in frail elderly (P = 0.032).
