Figure 1.
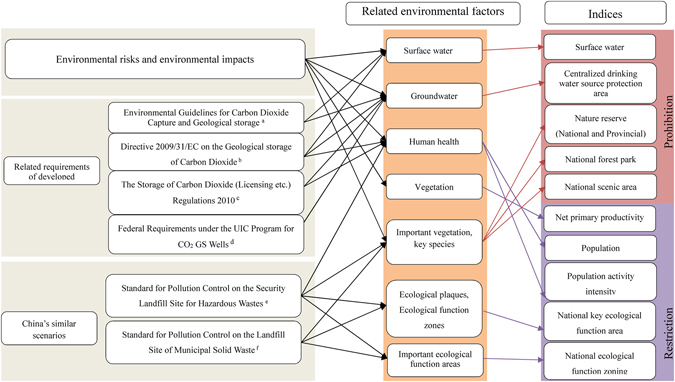
Factors and indices related to the environmental risks and effects of CO2 capture and storage. Note for Fig. 1: aThe Australian Environment Protection and Heritage Committee, Environmental Guidelines for Carbon Dioxide Capture and Geological storage — 2009, claims: all CCS projects must subject to environmental assessment during the legislative phase. All environmental risk assessment must contain an assessment of groundwater resources so as to protect regional water resources88. bEuropean Union, Directive 2009/31/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Geological Storage of Carbon Dioxide, claims: only areas with no significant risks of leakage and with no significant environmental and health risks can be selected as sequestration sites, and water resources or water protection areas should not be used for carbon dioxide sequestration89. cUnited Kingdom, The Storage of Carbon Dioxide (Licensing etc.) Regulations 2010, claims: licenses should not be issued for CO2 sequestration in water source areas; a sequestration license may be issued on the condition that the proposed sequestration site is free of leakage, environmental hazards and human health risks (http://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2010/2221/pdfs/uksi_20102221_en.pdf). dUS Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Requirements Under the Underground Injection Control (UIC) Program for Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) Geologic Sequestration (GS) Wells. The bill took effective on 10th January 2011 for geological storage wells of CO2. The purpose of this bill is to establish a new class, namely Class VI, to protect underground drinking water resources90. e Standard for Pollution Control on the Security Landfill Site for Hazardous Wastes (GB 18598-2001/XG1-2013)(China) claims74: site locations and distances from hazardous waste landfills to the surrounding population should be determined based on the conclusion of an environmental impact assessment, which should be identified and approved by the administrative department of environmental protection. The administrative approval will be treated as a basis for planning control. Landfill sites should not be selected in the area of urban planning and agricultural development, agricultural protection areas, nature reserves, scenic spots, heritage/archaeology conservation areas, protection areas for drinking water resources, long term planning areas for water supply, mineral resources districts and the other areas particularly in need of protection. fThe Standard for Pollution Control on the Landfill Site of Municipal Solid Waste (GB 16889-2008) (China) claims75: landfill sites should be consistent with regional environmental planning, environmental health facilities planning and local urban planning. Landfill sites should not be selected in areas of urban planning and agricultural development, agricultural protection areas, nature reserves, scenic spots, heritage/archaeology conservation areas, protection areas of drinking water resources, long term planning area for water supply, mineral resources districts, military sites, state secret areas and other zones that need special protection. The site selection of landfills should avoid wetlands.
