Fig. 6.
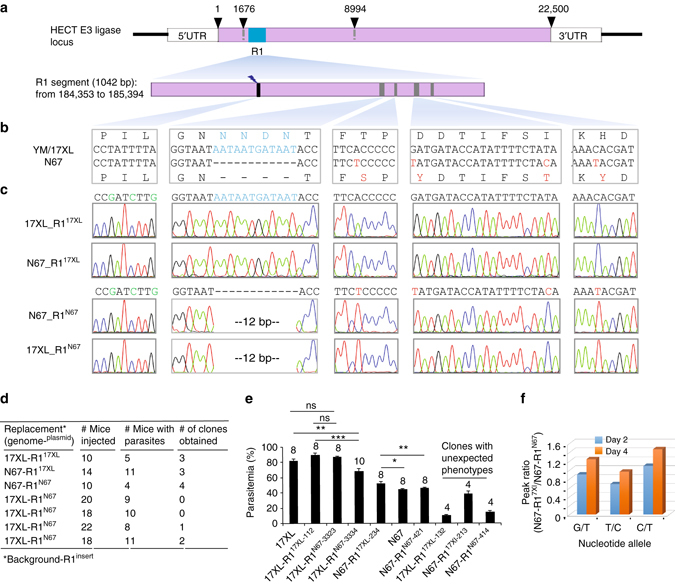
Replacement of a partial Pyheul gene segment alters parasite growth. a Diagram showing Pyheul gene structure and the region being replaced using the CRISPR/Cas9 method described previously37. The numbers on top of the gene bar are nucleotide positions indicating start and stop positions and the mapped region (1676–8994 bp). b Partial nucleotide and amino-acid sequences of guide RNA (gRNA) targeting site (black) and the polymorphic sites (dark green) between N67 and 17XL parasites within the R1 region. c Electropherograms of DNA sequences containing exchanged nucleotides in the self-replacement and cross-replacement parasite clones. Names of recombinant parasite clones are on the left. d Summary of allelic exchange experiments including the numbers of mice infected and parasite clones obtained. 17XL-R1N67 indicates R1 segment from N67 parasite replacing that of 17XL, and so on. Numbers of mice injected, numbers of mice injected with transfected parasites; numbers of mice with parasites, numbers of mice with parasites; numbers of clones obtained, numbers of parasite clones with correct modifications obtained. e Day-4 parasitemia (means and SE’s) of different parasite clones. The numbers on top of each bar indicate numbers of mice used. Two-sided t-test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. f Ratios of electropherogram peaks at three polymorphic nucleotides between N67 (T-C-T) and 17Xl (G-T-C) day 2 (blue, 17XL/N67) and day 4 (orange) post infection, showing increased proportions of N67-R117XL over N67-R1N67. Parasites were mixed at ~1:1 ratio. The graph represents two experiments of similar results
