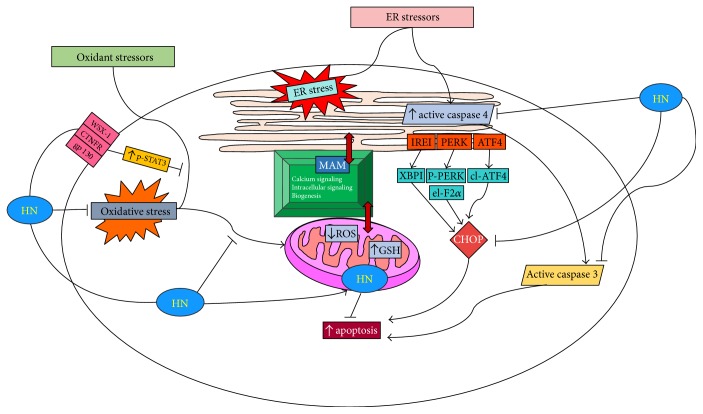
Figure 2.
HN inhibits OS and ER stress in RPE by direct and indirect mechanisms. ER and mitochondria are linked through MAMs (mitochondria-associated membranes) which perform a variety of functions; some of which are listed in the figure. ER stress leads to CHOP induction via multiple signaling mechanisms. ER stress also activates procaspase 4 to active caspase 4 which in turn upregulates active caspase 3 leading to increased apoptosis. Exogenous HN's action on the suppression of ER stress-induced apoptosis via inhibition of caspase 4, CHOP, and caspase 3 are also shown in the figure. Exogenous HN is taken up by RPE and gains entry into mitochondria when cotreated with oxidant stressor. HN downregulates cellular OS and decreases mitochondrial ROS and augments mitochondrial GSH. The receptor-mediated pathway of HN preventing oxidant-induced apoptosis via activation of phosphorylated STAT3 is also shown.