Figure 1. OX1R signaling attenuates KOR-induced reduction in cellular cAMP levels.
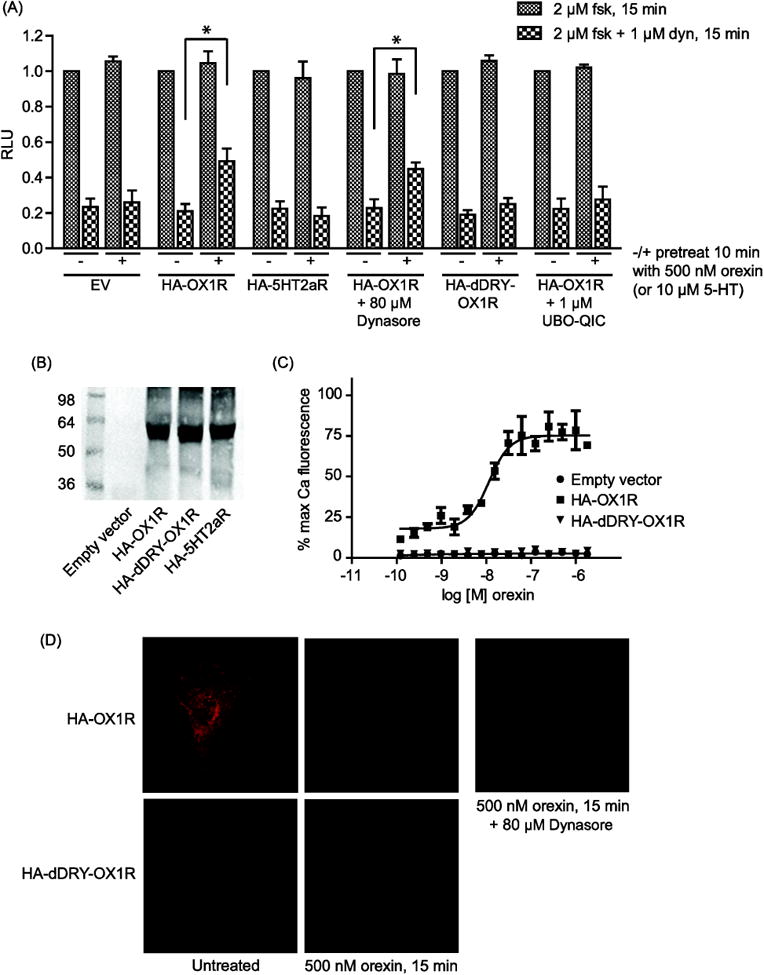
(A): CHO-KOR cells expressing ‘pGloSensor-22F’ cAMP sensor together with the indicated receptor construct or empty vector (EV) were incubated with or without 80 μM Dynasore or 1 μM Gq-inhibitor UBO-QIC for 2 h. Cells were pretreated or not with 500 nM orexin for 10 min prior to treatment with 2 μM forskolin (fsk) or 2 μM forskolin + 1 μM dynorphin (dyn) for 15 min, as indicated. Receptor expression was validated by western blot using a rat anti-HA antibody (Roche) (B). Data is normalized to the forskolin signal in the absence of orexin pretreatment for each transfection condition and error bars represent standard deviation from the mean of 3 separate experiments (* indicates p < 0.01). (C): HA-dDRY-OX1R fails to activate calcium signaling, consistent with a failure to activate Gαq. CHO cells were transfected as indicated and, after 48 h, treated with the indicated concentrations of orexin. Error bars represent standard error of the mean of 3 replicates and data shown is representative of 3 separate experiments. (D): CHO cells were transfected as indicated. After 48 h, cells were incubated with or without 80 μM Dynasore for 2 h then treated or not with 500 nM orexin for 15 min and fixed using PFA. Samples were analyzed by confocal microscopy using a rat anti-HA antibody (Roche) and an anti-rat Alexafluor-594 secondary antibody (Invitrogen).
