Fig. 5.
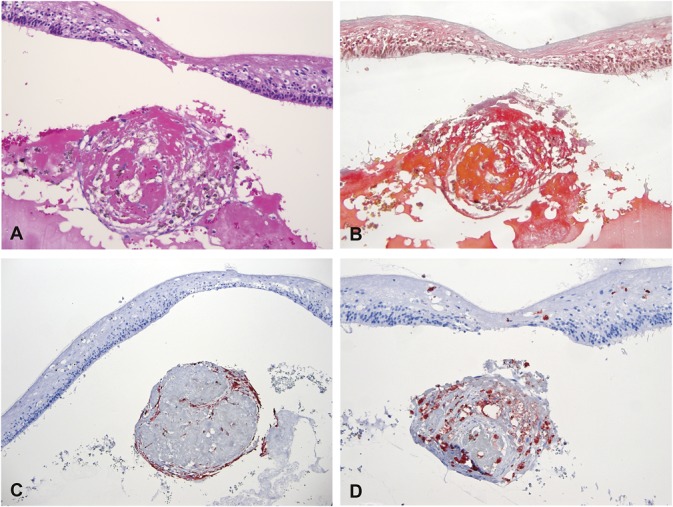
Histopathological analysis of a subfoveal nodule from an eye with Coats' disease. Specific stainings were performed for hematoxylin eosin (A, ×126), Martius Scarlett Blue (B, ×126), cytokeratins (AE1–AE3) (C, ×63), CD68 (D, ×126). The subfoveal lesion was formed by a round aggregate of proteinaceous material including fibrin (B) admixed with spindle cells, macrophages, and pigmented cells. Some of the cells within the lesion expressed pancytokeratins (C) consistent with a retinal pigment epithelium origin, while other expressed CD68 (D). Specific staining for endothelial cells was negative.
