Figure 2.
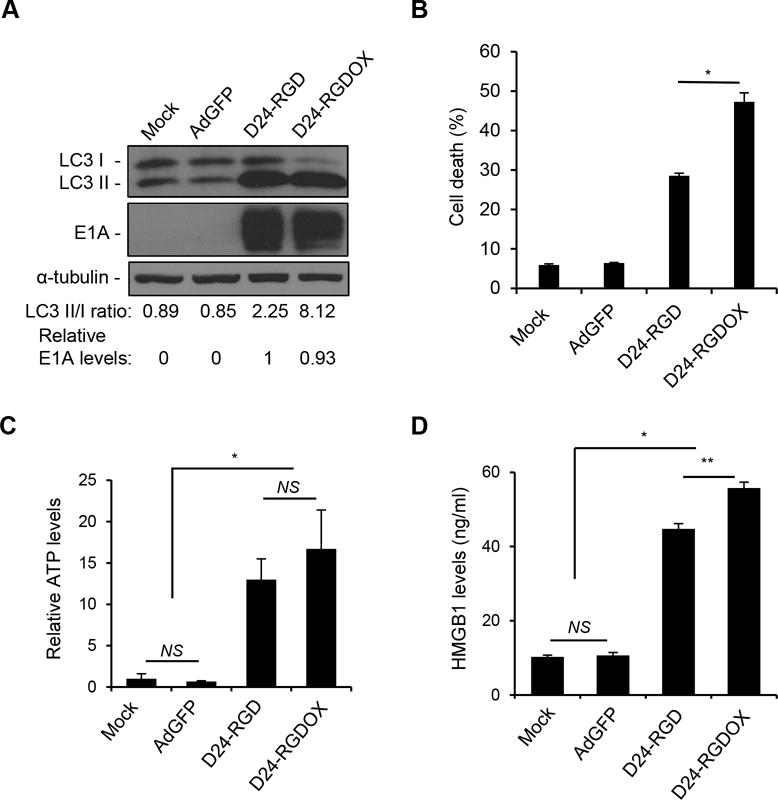
Immunogenic cell death induced by Delta-24-RGDOX. A, GL261 cells were infected with indicated viruses at 100 PFU/cell. 72 hours later, the cell lysates were analyzed with immunoblotting for the cytosolic form of microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 (LC3 I), or its phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate (LC3 II). The LC3 II/I ratio is used to monitor autophagy. The E1A levels were used as an indicator of the relative viral dose and normalized to the value in the D24-RGD group, which was set to 1. α-tubulin levels are shown as a protein loading control. AdGFP was used as a replication-deficient viral vector control. B, GL261 cells were infected with the indicated viruses at 100 PFU/cell. Cells were harvested after 72 hours and cell lysis (cell death) was monitored with ethidium homodimer-1 staining and analyzed with flow cytometry. C and D, To assess immunogenic cell death induced by the viruses, GL261 cells were infected with the indicated viruses at 100 PFU/cell. After 72 hours, the culture medium was collected and assayed for the amount of ATP (C) or HMGB1 (D). The relative ATP levels (C, 1 = average amount of ATP in mock-treated cells) and HMGB1 concentrations are shown (D). Values represent the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). NS: not significant (P ≥ 0.05); * P < 0.0002, ** P = 0.001, 2-tailed Student’s t test. Mock: PBS; D24-RGD: Delta-24-RGD; D24-RGDOX: Delta-24-RGDOX.
