Figure 3.
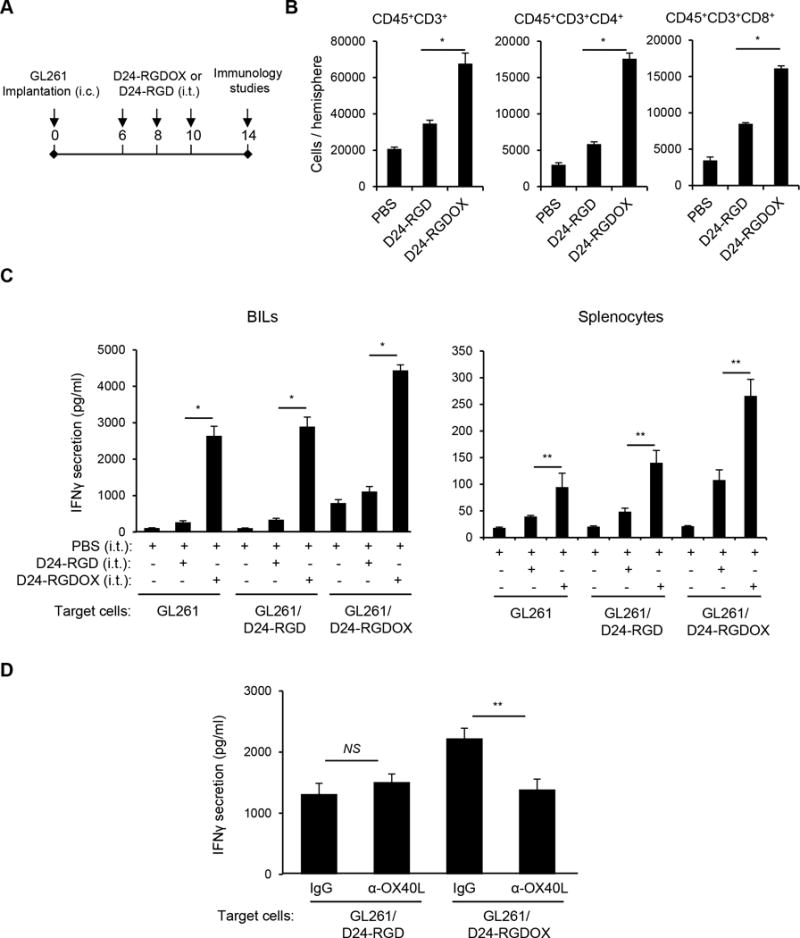
Anti-glioma immunity mediated by Delta-24-RGDOX. A, A cartoon depiction of the treatment scheme. i.c.: intracranial; i.t.: intratumoral. B, Brain-infiltrating leukocytes (BILs) from brain hemispheres with tumors of glioma-bearing mice treated with PBS or the indicated viruses (6 mice per group) were isolated. The BILs were examined using flow cytometry for the indicated cell surface markers to assess numbers of tumor-infiltrating lymphoctyes (CD45+CD3+), helper T lymphocytes (CD45+CD3+CD4+) and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CD45+CD3+CD8+) at the tumor site. C, BILs (left panel) or splenocytes (right panel) taken from the three groups of mice described in above (5 mice per group), were stimulated with pre-fixed GL261 cells that were uninfected, or had been infected with the indicated virus. Forty hours later, the concentration of IFNγ in the supernatant was assessed with ELISA. D, Inhibition of Delta-24-RGDOX-mediated activation of BILs by an anti-mOX40L antibody. BILs from hemispheres (taken from 9 mice) with Delta-24-RGDOX-infected tumors were isolated and stimulated with pre-fixed GL261 cells that had been infected with Delta-24-RGD or Delta-24-RGDOX in the presence of control immunoglobulin G (IgG) or an anti-mOX40L antibody (4 μg/ml). The concentration of IFNγ in the supernatant was assessed with ELISA. Values represent the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). NS: not significant (P ≥ 0.05); * P < 0.0001, ** P < 0.05, 2-tailed Student’s t test. D24-RGD: Delta-24-RGD; D24-RGDOX: Delta-24-RGDOX.
