Figure 5.
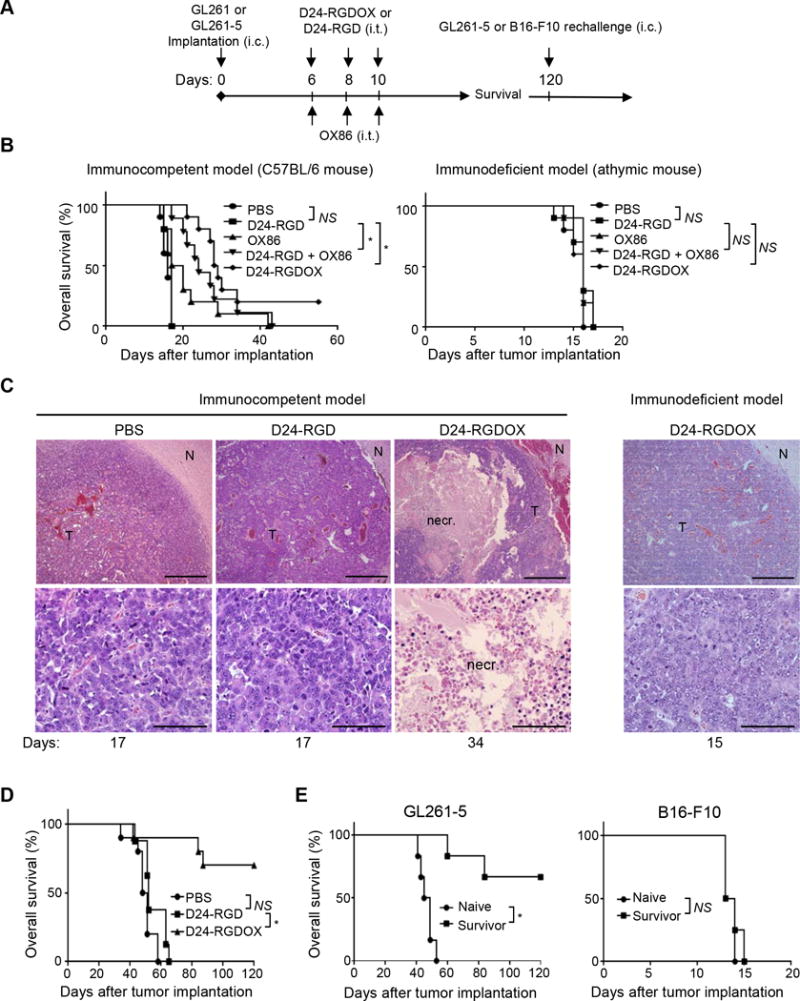
Anti-glioma activity of Delta-24-RGDOX. A, A cartoon depiction of the treatment scheme. i.c.: intracranial; i.t.: intratumoral. B, Survival plots of the different treatment groups in C57BL/6 (immunocompetent, left) or athymic (immunodeficient, right) mice (n = 10 per group, except n = 9 per group for OX86 + Delta-24-RGD in left panel). C, Delta-24-RGDOX-induced necrosis (necr.) in gliomas taken from C57BL/6 mice. Upper panel: representative hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections of the brains from treatment groups showing tumor (T) and normal brain (N) tissue. Lower panel: enlarged images of areas within the tumor. Representative results from at least 6 mice from each group in B are shown. The numbers at the bottom indicate the number of days between tumor implantation and the sacrificing of the mice. Scale: upper panel, 200 μm; lower panel, 50 μm. D, Survival plots of mice in the treatment groups bearing slow-growing GL261-5 gliomas. n = 10, except for Delta-24-RGD, where n = 8. E, Survival plots for mice treated with Delta-24-RGDOX after being re-challenged with GL261-5 (left panel, n = 6) or B16-F10 (right panel, n = 4) cells. NS: not significant (P ≥ 0.05); * P < 0.001, log-rank test. D24-RGD: Delta-24-RGD; D24-RGDOX: Delta-24-RGDOX.
