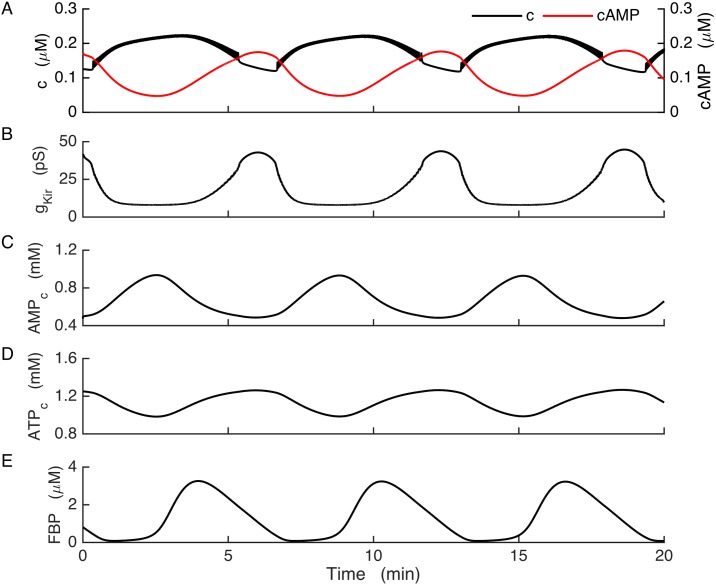
Fig 5. Bursting in the model KO cells, where K(ATP) current is replaced with Kir2.1 current.
Glycolytic oscillations drive bursting through a cAMP-dependent pathway. (A) Ca2+ and cAMP concentrations oscillate in anti-phase. (B) Conductance of the Kir2.1 current, time averaged over a window of 6 s to remove fast variations and highlight the cAMP-dependent slow dynamics. (C) AMPc oscillations contribute to the production of cAMP oscillations. (D) ATPc oscillates due to oscillations in glycolysis. (E) FBP is the product of the PFK enzyme that is responsible for glycolytic oscillations. For this simulation, the glucokinase reaction rate was increased from 0.09 μM/ms to 0.14 μM/ms and kFBP was increased from 0.8 to 0.95.