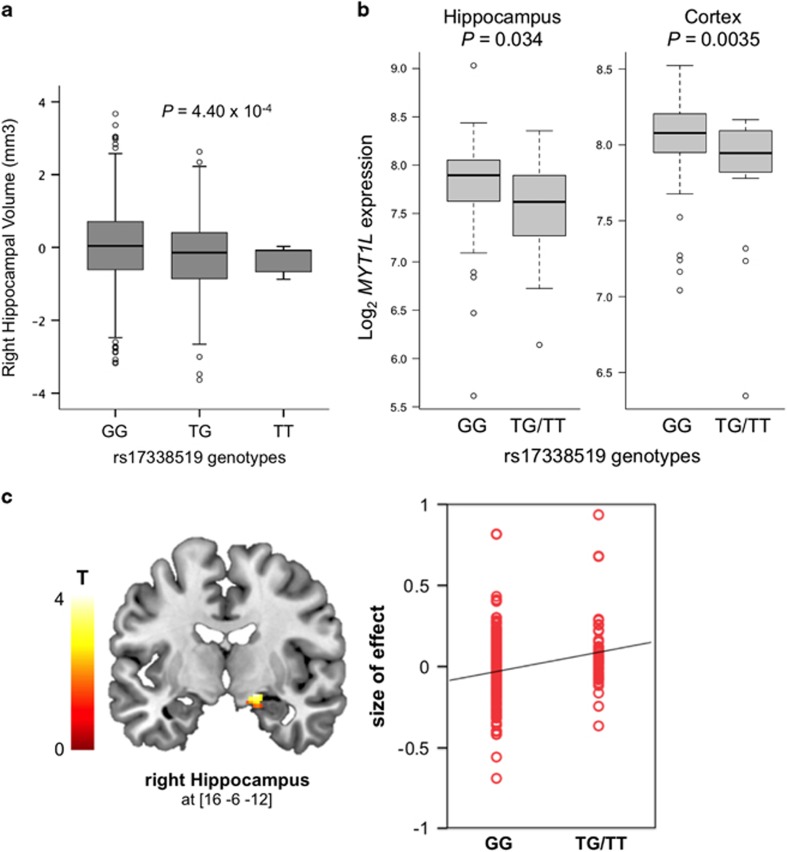
Figure 5.
Associations between MYT1L expression and hippocampus volume and hippocampus activation during episodic memory recall. (a) Association of rs17338519 with hippocampal volume in a sample of N=1,398 adolescents. Linear regression analyses indicated that the number of minor T-alleles associated with lower volume of the right hippocampus (P=4.40 × 10−4). (b) Expression of MYT1L stratified by genotypes at rs17338519, in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex of 134 post-mortem human brains. For the cortex, expressions of MYT1L in the occipital, temporal, and frontal cortices were averaged. Regression analyses indicated that the presence of the T-allele at rs17338519 associated with decreased MYT1L mRNA levels in the hippocampus (P=0.034) and the cortex (P=0.0035). Genotypes count: GG=110; T-carriers=24. (c) Association of rs17338519 with hippocampal activation during an fMRI task of episodic memory recall in 285 healthy adults. The left panel shows the ROI-derived brain activation map within the hippocampus, with increased activation of the right hippocampus (x=16, y=−6, z=−12) during episodic memory recall in carriers of the T-allele (N=285; p=0.02 FWE corrected for multiple testing across ROI). The right panel shows a quantification of rs17338519 genotypes effects on the activation of the right hippocampus. Each dot represents size of effect in one subject.