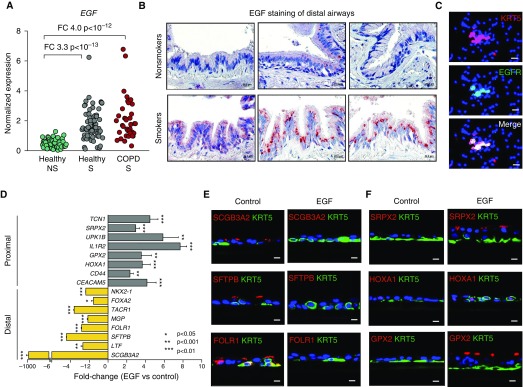
Figure 5.
Epidermal growth factor (EGF)/epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling in small airway epithelium (SAE) basal stem cells (BCs) promotes smoking-associated distal (D)-to-proximal (P) repatterning phenotype. (A) Microarray-based EGF gene expression in the SAE of healthy nonsmokers (NS; n = 63), healthy smokers (S; n = 73), and smokers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD-S; n = 37). Fold changes (FCs) and Benjamini-Hochberg–corrected P values are shown. (B) Representative images showing EGF expression in the D airways of NS and S (n = 3 per group) using immunohistochemistry. (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of SAE brushing samples from healthy NS for BC marker keratin 5 (KRT5) and EGFR. In B and C, scale bar = 20 µm. (D) FC in expression of selected P- and D-signature genes in the epithelium derived from SAE BCs during 28 days of air–liquid interface culture in the presence of EGF (10 ng/ml) versus control BCs (n = 3 experiments). See Figures E9C and E9D for air–liquid interface time-course data and more examples. (E and F) Airway epithelium derived from control and EGF-treated SAE BCs as described in D analyzed using immunofluorescence for expression of indicated (E) D and (F) P signature genes (red), BC marker KRT5 (green), and nuclei (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole [blue]). In E and F, scale bar = 10 µm. FOLR1 = folate receptor 1; GPX2 = glutathione peroxidase 2; HOXA1 = homeobox A1; SCGB3A2 = secretoglobin family 3A member 2; SFTPB = surfactant protein B; SRPX2 = sushi repeat-containing protein X-linked 2.