Figure 4.
Treatment of Human Skin Explants with 37.5 mM of SIK Inhibitor Induces Pigmentation
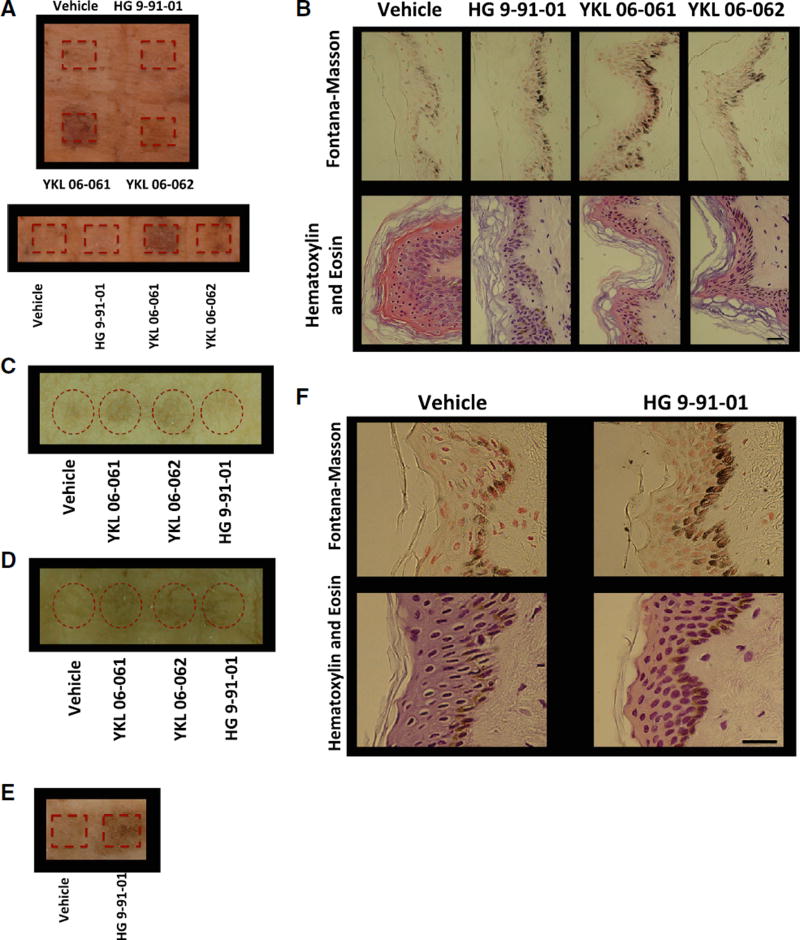
(A) Human breast skin explants treated with passive application of vehicle control (70% ethanol, 30% propylene glycol) or 37.5 mM SIK inhibitor YKL 06-061, YKL 06-062, or HG 9-91-01 for 8 days (10 µL; 1×/day). Image was taken 2 days after the end of treatment (image is representative of two of n = 3 experiments).
(B) Fontana-Masson (top panel) and H&E (bottom panel) staining (magnification, 400×) of breast skin described in (A). Scale bar represents 25 µm.
(C) Human breast skin explants treated with passive application of vehicle control or 37.5 mM SIK inhibitor YKL 06-061, YKL 06-062, or HG 9-91-01 for 5 days (10 µL; 2×/day). Image was taken 1 day after the end of treatment (image is representative of n = 1 experiment).
(D) Human breast skin explants treated with passive application of vehicle control or 37.5 mM SIK inhibitor YKL 06-061, YKL 06-062, or HG 9-91-01 for 6 days (10 µL; 2×/day). Image was taken 1 day after the end of treatment (image is representative of n = 1 experiment).
(E) Human breast skin explants treated with mechanical application of vehicle control or 50 mM (50 µL for 1 day; 1×/day) or 25 mM (50 µL for 3 days; 3×/day) HG 9-91-01. Image was taken 4 days after the start of treatment (image is representative of n = 1 experiment).
(F) Fontana-Masson (top panels) and H&E (bottom panels) staining (magnification, 400×) of human skin explants described in (E). Scale bar represents 25 µm.