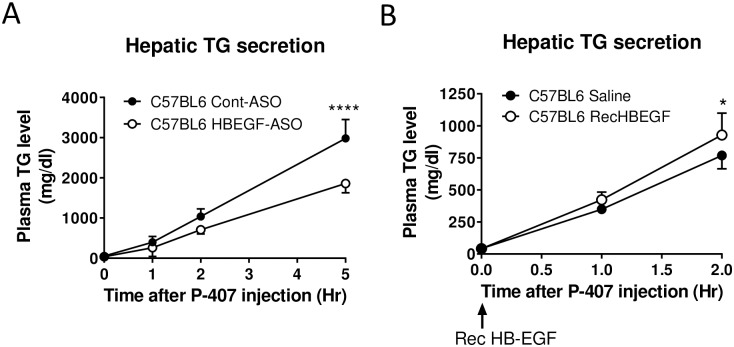
Fig 4. HB-EGF targeting using ASO administration induced suppression of hepatic VLDL-associated TG secretion rate.
(A) C57BL/6 mice (male, 10 weeks of age) were pretreated with control and HB-EGF ASOs for 6 weeks (40 mg/kg/week). For the secretion assay, a lipoprotein lipase inhibitor poloxamer-407 (P-407) (1.0 g/kg of body weight) was injected intraperitoneally and he changes of TG levels in the plasma were determined for 0–5 hours (N = 3–5 per group). (B) C57BL/6 mice (male, 10 weeks of age) were tail-vein injected with recombinant HB-EGF (2 mg/kg of body weight) at 0 hour point of P-407 injection. The TG levels in the plasma samples for 0–2 hour points were determined (N = 5 per group). * p<0.05; and **** p<0.0001.