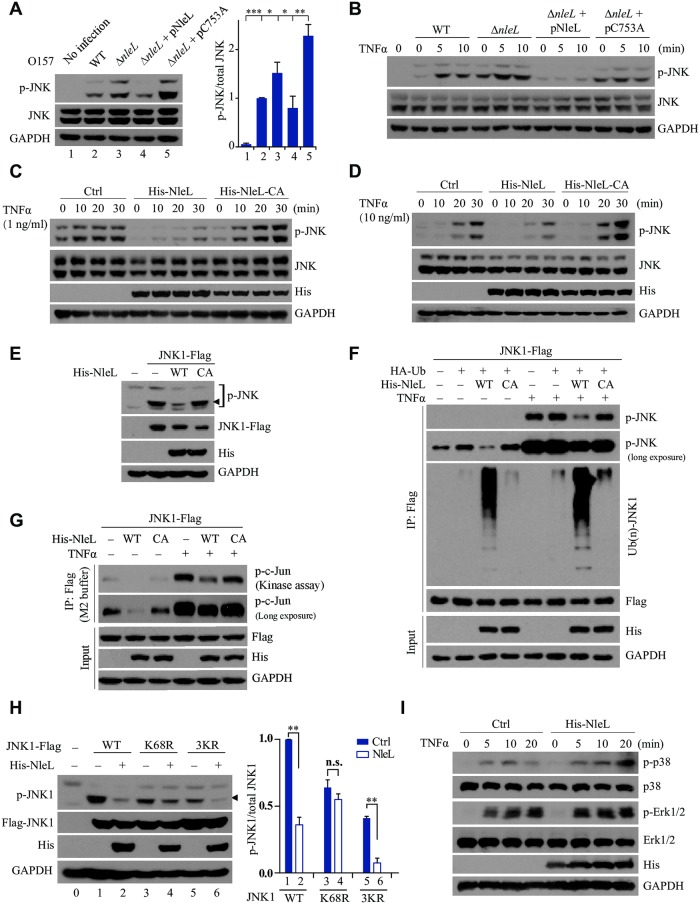
Fig 3. NleL-mediated JNK1 ubiquitylation inhibits phosphorylation of JNK1.
(A) The ΔnleL strain of EHEC O157:H7 induced higher level of JNK phosphorylation than wild-type strain. Cells were infected with indicated EHEC strains with MOI of 100:1 for 2.5 h, and further sub-cultured 2 h in fresh DMEM medium. Then infected cells were lysed and subjected to IB analysis with indicated antibodies (left). The phosphorylated-JNK/ total JNK ratio (right) were calculated by quantifying protein bands. The lane numbers correspond to those shown in the left diagram. Bars represent means ± s.d., *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (Student’s t-test, data are from three independent experiments, (n = 3)). (B) Cells were infected by indicated EHEC strains and then subjected to TNFα (10 ng/ml) treatment at the indicated time points. (C and D) NleL inhibited TNFα-mediated JNKs phosphorylation. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding His-NleL or C753A mutant for 24 h. Cells were then stimulated by TNFα (1 ng/ml, C or 10 ng/ml, D). (E) Wild-type NleL, but not the C753A mutant, inhibited basal phosphorylation of ectopically expressed JNK1 in HEK293T cells. (F) NleL-induced JNK1 ubiquitylation conversely correlates with JNK1 phosphorylation. Indicated plasmids were transfected to HEK293T cells for 24 h. After transfection, cells were stimulated by TNFα (10 ng/ml) for 10 min and lysed in denatured RIPA buffer. Cell lysate was subjected to anti-Flag IP to enrich JNK1 protein. Phosphorylation and ubiquitylation status of JNK1 was assayed with indicated antibodies. (G) The E3 activity of NleL inhibits JNK activity. Plasmids expressing Flag–tagged JNK1 and His6-tagged NleL or its C753A mutant were co-transfected to HEK293T cells. 24 h after transfection, cells were treated with or without TNFα (10 ng/ml) for 10 min. Cells were then washed once in PBS and lysed in M2 buffer. Cell lysates were subjected to IP with anti-Flag M2 beads overnight. The anti-Flag M2 beads were then washed five times with M2 buffer, twice with 20mM Hepes (pH 7.4) and then subjected to the in vitro kinase assay, using GST-tagged c-Jun (1-79aa) as the substrate. The phosphorylation status of c-Jun was detected by anti-p-c-Jun antibody. (H) NleL did not suppress the TNFα-stimulated phosphorylation of K68R mutant of JNK1. HEK293T cells transiently expressed wild-type Flag-tagged JNK1 or its indicated mutants (K68R and 3KR). Cells were treated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) for 10 min. Phosphorylation of JNK1 was detected by immunoblotting analysis with anti-p-JNK antibody, and the phosphorylated-JNK1/ total JNK1 ratio (right) were further quantitated. The lane numbers correspond to those shown in the left panel. Bars represent means ± s.d., **P < 0.01, n.s., not significant. (Student’s t-test, data are from at least three independent experiments, (n = 3)). (I) NleL had no effect on TNFα-induced phosphorylation of p38 and Erk in mammalian cells. Cells were transfected with or without the plasmids encoding His6-tagged NleL for 24 h, and then subjected to TNFα treatment (10 ng/ml) at indicated times. Phosphorylation status of endogenous p38 or Erk was determined by IB with respective antibodies. Blots are representative of at least three independent experiments.