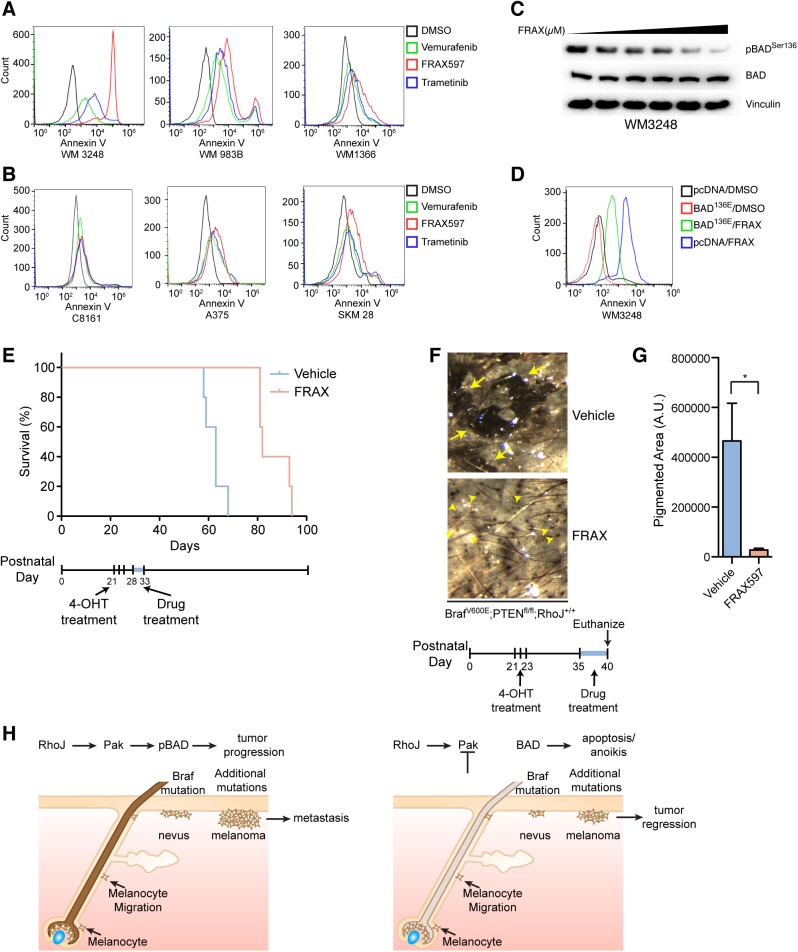
Fig 5. PAK inhibition induces apoptosis via BAD and blocks the progression of BRAF mutant melanomas.
(A) FRAX597 inhibits PAK1 activation and induces apoptosis in BRAFV600E melanoma cell lines. Apoptosis was quantified with annexin-V labeling and flow cytometry. (B) FRAX597 does not induce apoptosis in cell lines that do not express detectable RhoJ. Flow cytometry analysis of melanoma cell lines treated with vehicle, vemurafenib (5μM), FRAX597 (1μM), or trametinib (0.1μM). (C) PAK inhibition decreases the phosphorylation of BADSer 136. Melanoma cell line WM3248 harboring the BRAFV600E mutation was treated with an increasing concentration of FRAX597 (0μM, 0.2μM, 0.5μM, 1μM, 2.5μM, 5μM) and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (D) Over expression of pcDNA3 BADS136E phosphomimetic rescued survival after FRAX597 treatment. Cells were transfected with Lipofectamine 3000 according to the manufacturer’s instructions and treated with FRAX or DMSO. Apoptosis was measured with flow cytometry. (E) PAK inhibition prolongs survival in BrafV600E PTEN null mice. Melanoma was induced in adult mice at P21, P22, and P23 with topical treatment of 4-OHT (25mg/mL) as previously described (18). Vehicle or FRAX597 (100mg/kg P.O. Q.D.) was administered for six days between P28 and P33. Mice were euthanized when the tumor burden exceeded the minimum restrictions as advised by veterinary technicians, and Kaplan-Meier survival curves were generated for BrafCA/+; Ptenfl/fl; Tyr::CreERT2; RhoJ+/+ vehicle (n = 5) or FRAX597 (n = 5) treated animals. Log-rank test demonstrates significant difference between the two groups (**p<0.002, Log-rank test). (F) PAK inhibition delays tumor formation. Mice were treated with 4-OHT at P21, P22, and P23 on their backs to induce melanoma. Tumors were allowed to progress for 2 weeks prior to drug treatment. Mice were either administered FRAX597 or Vehicle for six days. Mice were euthanized after six days of drug treatment and images were taken with a dissecting microscope. Tumors were visible in vehicle treated mice (arrows) but smaller lesions were visible FRAX597 treated mice (arrowheads). (G) Disruption of RhoJ-PAK signaling blocks the formation of nevi and the growth of melanoma. The area of pigmented lesions (developing melanomas) from F was quantified (A.U. arbitrary units) and analyzed (*p = 0.04, n = 3, Student t-test). Error bars indicate SEM. (H) RhoJ expression enables melanocytes to differentiate and migrate out of the hair follicle during the process of nevogenesis and evolve into melanoma tumors. Perturbation of RhoJ-Pak signaling prevents melanocytes from differentiating normally, which leads to loss of pigment in hair, impairment of melanocytes to migrate out of the hair to form nevi, and prevent transformation into melanoma as efficiently.