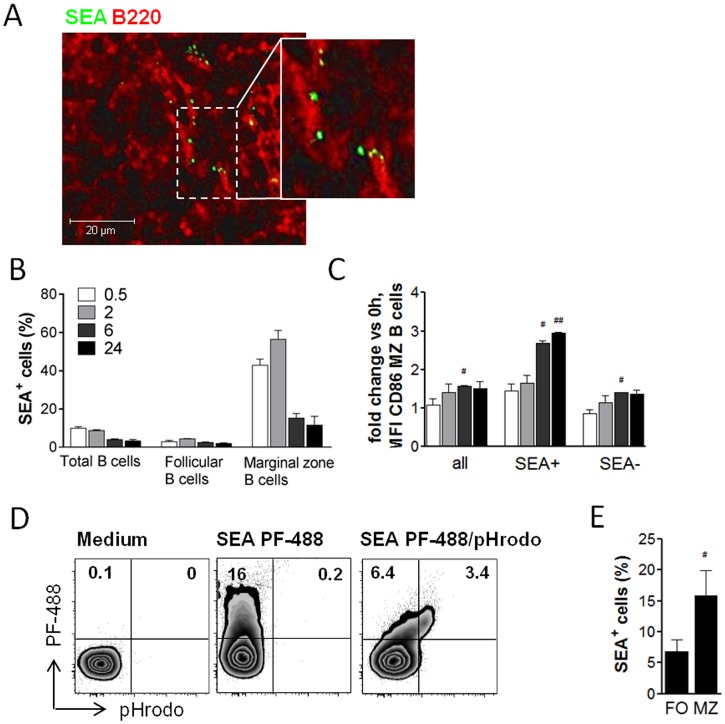
Fig 4. Schistosome antigens bind to B cells and are internalized into acidic compartments.
(A) C57BL/6 mice were i.v. injected with 200 μg of fluorescently labeled SEA and spleens snap-frozen 30 minutes later. Fluorescence microscopic image shows localization of SEA to B220+ B cells and is representative for 2 experiments with N = 5 mice and 3 viewing fields per section imaged. (B, C) Splenic B cells were analyzed by flow cytometry at 30 minutes to 24 hours after i.v. injection of labeled SEA for (B) frequency of SEA+ cells within total B cells or B cell subsets as gated in Fig 2A, and for (C) fold increase of CD86 expression on total MZ B cells compared to MZ B cells gated for SEA+ and SEA- populations. Summary of 2 experiments with N = 2. (D, E) Splenic B cells from naïve mice were cultured in vitro with SEA (20 μg/ml) labeled with a green dye (PF-488) alone, or co-labeled with a pH-sensitive dye (pHrodo Red). After 60 minutes, the frequency of SEA+ B cells was determined by flow cytometry. (D) Gated for total CD19+ B cells (1 representative out of 2 experiments shown). (E) Gated for follicular (FO) and marginal zone (MZ) B cell subsets (summary of 3 experiments). Significant differences indicated with # p < 0.05 and ## p < 0.01 are determined by one-sample t-test of log-transformed data (C) or between B cell subsets by Wilcoxon paired test.