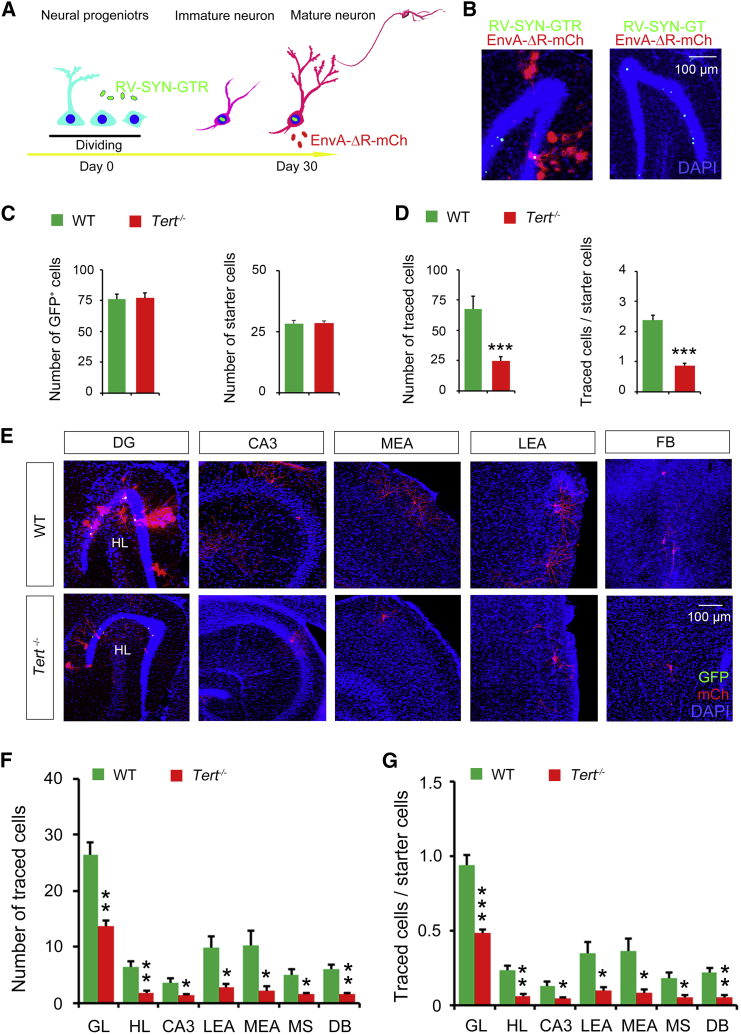
Figure 5.
Deletion of TERT Gene Impairs Afferent Circuit Incorporation of Hippocampal Newborn Neurons
(A) A diagram showing the dual-virus retrograde tracing system used to trace afferent cells of hippocampal newborn neurons.
(B) Representative photos showing the GFP+ cells, starter cells, and traced cells in the DG after injection of RV-SYN-GTR and EnvA-ΔG-mCh (left). As control, RV-SYN-GT lacking rabies glycoprotein was injected 30 days before EnvA-ΔG-mCh injection. No starter cells or traced cells were observed in this situation.
(C and D) Bar graphs showing the number of GFP+ cells and starter cells in the DG of Tert−/− or WT mice. n = 4, Student's t test (C). Bar graphs showing the number of traced cells (∗∗∗p = 0.0004) and the ratio of traced cells/starter cells (∗∗∗p = 0.0001) in Tert−/− or WT mice. n = 4 independent experiments, Student's t test (D).
(E–G) Representative images showing the distribution of input cells throughout the brain (E). Bar graphs showing the number of traced cells (F) and the ratio of traced cells/starter cells (G) in regions of the brain. n = 4 independent experiments, Student's t test for each region. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. DG, dentate gyrus; HL, hilus; MEA, medial entorhinal area; LEA, lateral entorhinal area; MS, medial septum; DB, diagonal band.
Error bars, SEM.