Figure 2.
Transcriptional Profile of hiPSC-Astrocytes and Primary Human Fetal Astrocytes
RNA-seq analysis of hiPSC-derived NPCs (n = 8), neurons (n = 6), and astrocytes (n = 4) together with pAstrocytes from human fetal cerebral cortex and midbrain.
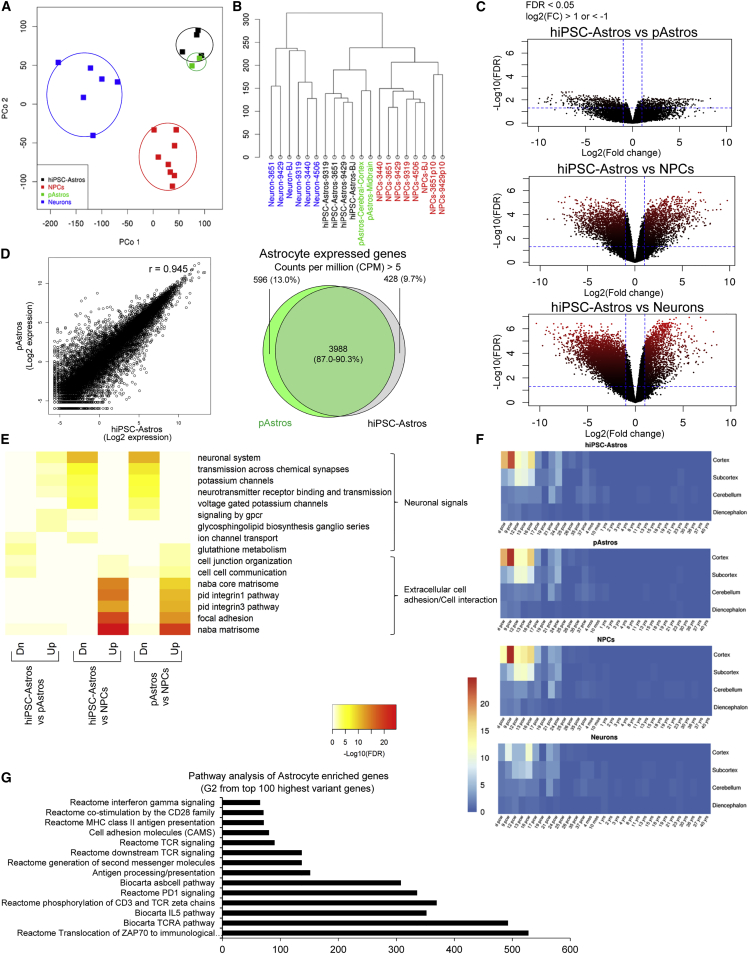
(A and B) Principal component (P.Co) analysis (A) and clustering diagram (B) of hiPSC-derived NPCs, neurons, and astrocytes, together with pAstrocytes.
(C) Volcano plot comparison of hiPSC-astrocytes to pAstrocytes (top), as well as to hiPSC-derived NPCs (middle) and neurons (bottom). Average log2(fold change) versus −log10(FDR) is shown for all genes. Genes upregulated and downregulated by 2-fold change and FDR < 0.05 are labeled by red dots. The number of genes differentially expressed between different cell types is indicated by the red color density and quantified in Figure S2B.
(D) Scatterplot (left) comparing gene expression in hiPSC-astrocytes and pAstrocytes. r represents the Spearman correlation coefficient. Venn diagram (right) of overlapping gene expression (CPM > 5) between hiPSC-astrocytes and pAstrocytes.
(E) Functional pathway enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes between hiPSC-astrocytes and pAstrocytes (left), hiPSC-astrocytes and NPCs (middle), and pAstrocytes and NPCs (right); hiPSC-astrocytes and pAstrocytes express increased extracellular cell communication signals, but decreased neuronal signals relative to NPCs.
(F) Heatmap produced by Wilcoxon's rank-sum comparisons of hiPSC-derived NPCs, neurons, and astrocytes, as well as pAstrocytes, relative to the Allen BrainSpan Atlas.
(G) Fold enrichment from functional pathway analysis of astrocyte-enriched genes, group G2 sorted from top 100 most variable genes from Figure S3A and Table 2.