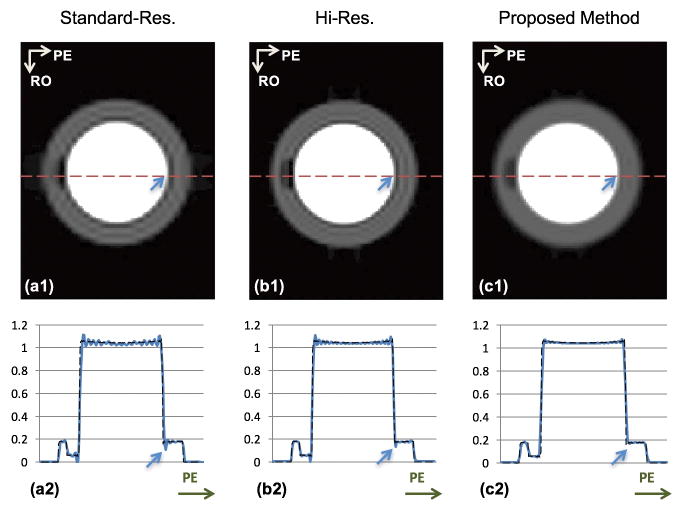
FIGURE 3. Numerical simulation results.
The top row shows the reconstructed images corresponding to the standard-res, hi-res, and proposed schemes. The bottom row shows a 1D cut along the PE direction for the respective images, super-imposed on the “ground truth” signal intensity profile (arrows show corresponding pixel positions along PE). (a1,a2): Reconstruction of the analytical phantom with standard-res acquisition corresponding to the conventional method; (b1,b2): Non-apodized reconstruction with hi-res acquisition; (c1,c2): Apodized reconstruction of the hi-res acquisition (same k-space data as in Panels b1,b2) corresponding to the proposed method. Compared to the standard-res image in (a1,a2), the DRA (Gibbs ringing) is effectively eliminated in the apodized hi-res image in (c1,c2). The reconstructed resolution is the same between (a1) and (c1). Comparing (b1) versus (c1), the hi-res image still shows a thin but noticeable DRA. After apodization, Gibbs ringing is significantly suppressed (consistent with Fig. 2).