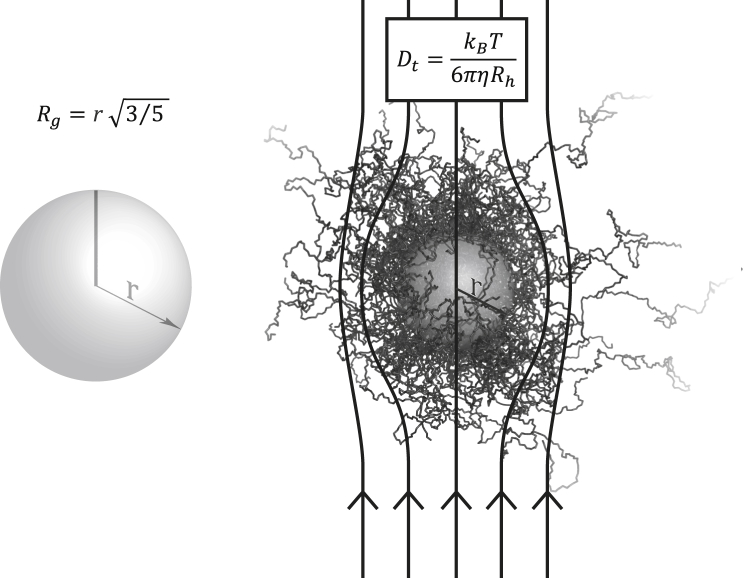
Figure 1.
Visual representation of the radius of gyration and hydrodynamic radius. (Left) The radius of gyration (Rg) of an object can be calculated as the root mean-square distance between each point in the object and its center of mass. Thus, for a protein, it directly reports on the typical distance between an atom and the center of mass of the protein. In the case of a solid sphere, . (Right) The Stokes radius or hydrodynamic radius (Rh) of a solute is the corresponding radius of a hard sphere that diffuses at the same rate as that solute. Dt is the translational diffusion coefficient.