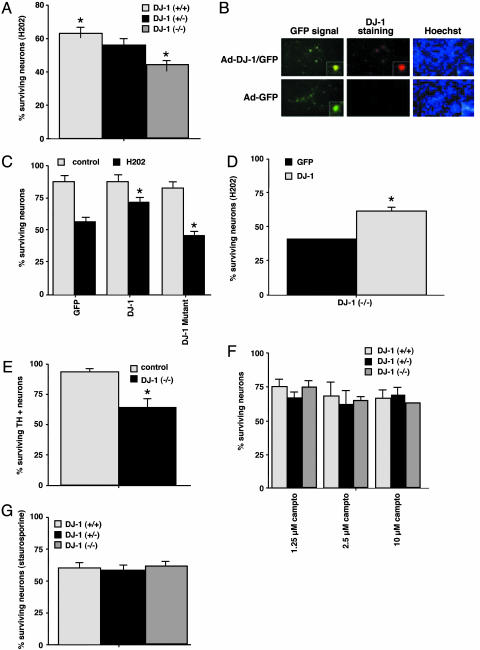
Fig. 1.
DJ-1 protects against cell death induced by oxidative, but not nonoxidative, stress. Survival determinations for each of the following experiments are described in Experimental Procedures. (A) Increased sensitivity to H2O2 in the absence of DJ-1. Cortical neurons from DJ-1+/+, DJ-1+/–, and DJ-1–/–embryos were treated for 3 h with 30 μM H2O2. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of DJ-1+/+ embryonic cortical neurons infected with an adenoviral vector (Ad) expressing either GFP or GFP plus DJ-1. Hoechst nuclear staining of the same culture is also shown. (C) Protective effect of DJ-1 overexpression in DJ-1+/+ cortical neurons. DJ-1+/+ neurons infected with adenovirus expressing GFP plus WT DJ-1 protein, but not GFP plus mutated (L166P) DJ-1 protein, showed increased survival after H2O2 exposure. Control, no H2O2. (D) Protective effect of WT DJ-1 in DJ-1–/–cortical neurons. DJ-1–/–neurons infected with adenovirus expressing GFP plus WT DJ-1 showed increased survival after H2O2 exposure. (E) Increased sensitivity of DJ-1–/–mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons (TH+) to other oxidative insults. DJ-1–/–cortical neurons were exposed to 10 nM rotenone for 24 h. (F and G) Lack of sensitivity of DJ-1–/–cortical neurons (TH+) to nonoxidative insults. The indicated doses of camptothecin (Fig. 1F) or 2 μM staurosporine (Fig. 1G) were applied to DJ-1+/+, DJ-1+/–, and DJ-1–/–neurons for 16 h. For A and C–G, each data point is the mean ± SEM of three to five independent cultures, where * denotes a significance level of P < 0.05.