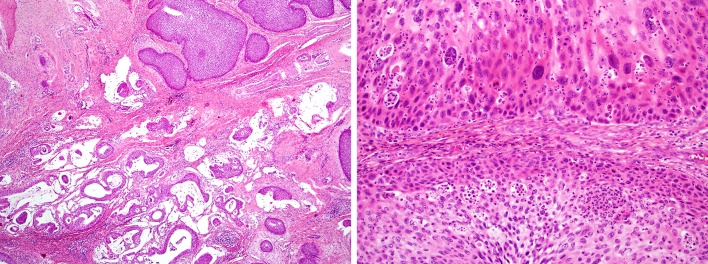
Fig. 4.
Carcinoma ex-inverted sinonasal papilloma. In this unusual example, an invasive mucin-producing adenosquamous carcinoma (bottom) is arising in association with an inverted sinonasal papilloma (top). This figure underscores that while squamous cell carcinomas are most common, unusual carcinomas can arise from inverted sinonasal papillomas. a Squamous cell carcinoma ex-inverted sinonasal papilloma (top) exhibits increased nuclear pleomorphism, prominent nucleoli and increased mitotic activity when compared to the inverted sinonasal papilloma (bottom). The papilloma component exhibits increased cellular atypia in the basal layer, a change that may be regarded as squamous dysplasia (b)