Figure 6.
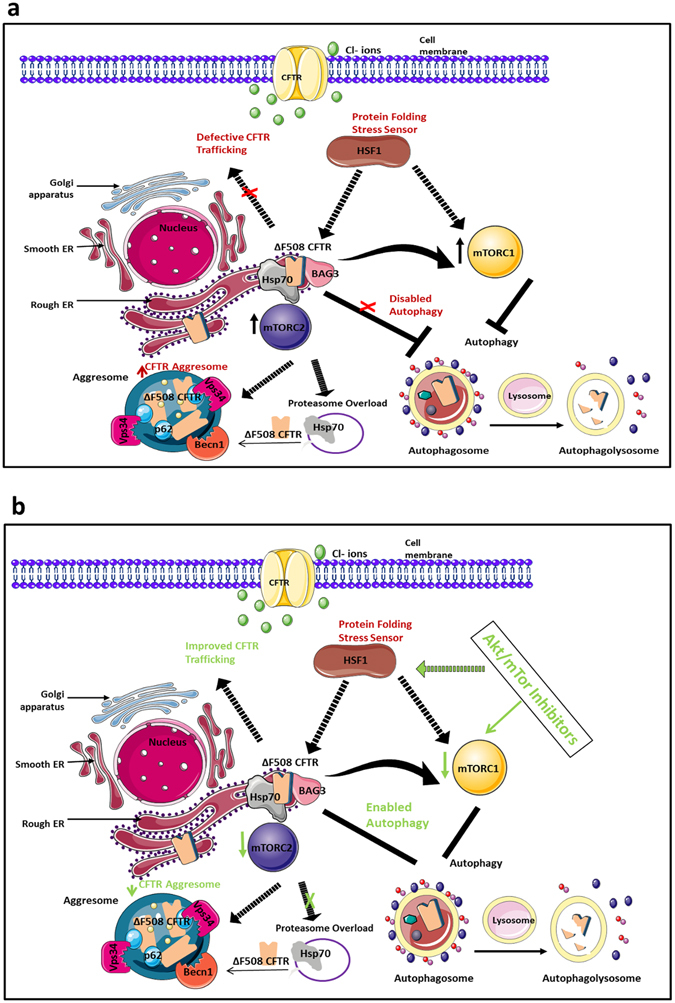
Regulation of ΔF508 CFTR stability by inhibitors to the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. (a) The ΔF508 variant of CFTR is characterized by ER accumulation, misfolding and an inability to traffic correctly to the plasma membrane where it functions as a chloride channel. It is believed that ΔF508 CFTR is retained in the ER in a Hsp70/90-containing chaperone trap influenced by the stress response sensor Heat Shock Factor (HSF1). Degradation of CFTR by the ERAD machinery is favoured but when CFTR that cannot be degraded by the proteasome machinery, (proteasome overload), CFTR can be stocked in the cytoplasm in the form of aggresomes. Our results indicate that mTORC1/2 signalling is upregulated in ΔF508 CFBE cells which have a defective autophagy pathway. Defective autophagy has been connected to reduced aggresome clearance. We observed CFTR localisation within aggresomes in ΔF508 CFBE41o- cells under conditions of proteasome inhibition. (b) In the presence of inhibitors to the PI3K/AKT/mTOR (eg MK-2206) we observed a decrease in mTORC1/2 activation and a corresponding increase in autophagic activity. We detected an increase in CFTR stability/trafficking upon therapeutic intervention of this pathway. We also revealed that HSF1 and BAG3 expression (which is stimulated by HSF1) are potentially regulated by PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors. These data suggest that selective PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors, such as MK-2206, may improve CFTR stability by both restoring autophagy through inhibition of mTOR and through the HSF1/BAG3 axis which, in turn, can regulate autophagy and ΔF508 CFTR aggregates. This figure was produced, in part, by using Servier Medical Art, (www.servier.com/Powerpoint-image-bank).
