Fig. 1.
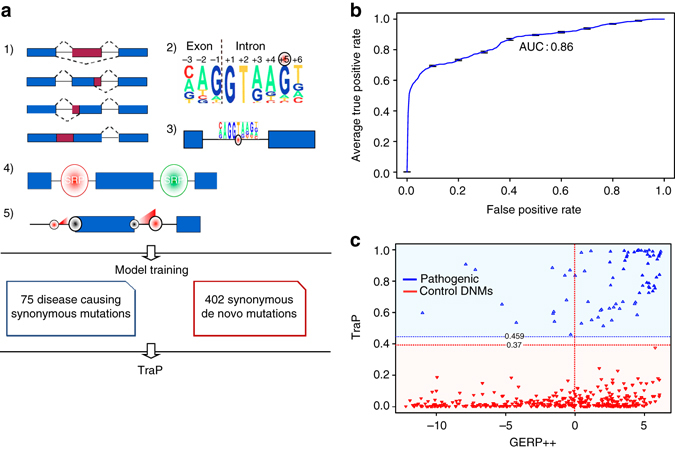
TraP model construction and evaluation. a TraP construction workflow and main features calculated for TraP: (1) Information acquisition from all genes and transcripts that harbor by the variant, (2) changes to splice site motif that affect it’s binding affinity to the splicing machinery, (3) creations of new splice junctions that might interact with the splicing machinery, (4) creations and disruptions of cis-acting binding sites to splicing regulatory proteins (SRP), (5) interactions between features, such as a stronger effect of a new splice site on an exon with a weak original splice site (red representing a new splice site). Model is trained using synonymous variants that are either known pathogenic variants (blue box, left) or DNMs from healthy individuals (red box, right). b A receiver-operating characteristic curve showing the results of 10 rounds of 10-fold cross-validations with an average AUC of 0.86. c Model predictions of the training-set show a clear separation of pathogenic variants (blue) versus control DNMs (red). TraP (y-axis) exhibits a minimum threshold for pathogenic variants of 0.459, below, which reside all control DNMs. GERP++ score (x-axis) considers 49.5% of benign variants as conserved
