Figure 2.
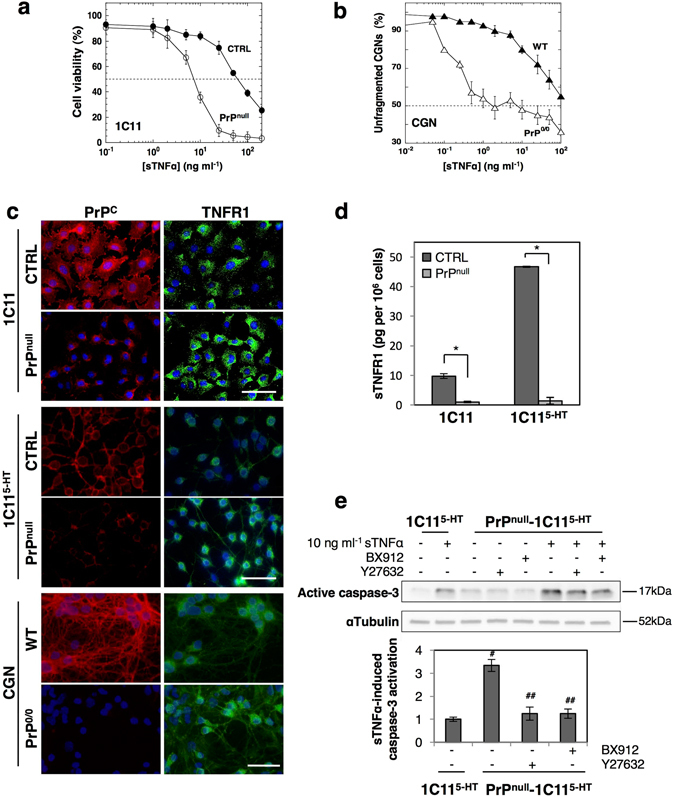
Loss of PrPC exacerbates cell sensitivity to sTNFα by reducing TNFR1 shedding in a ROCK-I- and PDK1-dependent manner. (a) Reduced viability of PrPnull-1C11 cells after exposure to increasing sTNFα concentrations for 72 h as compared to 1C11 cells (CTRL). (b) Increased dendritic fragmentation in PrP0/0-CGNs after exposure to increasing concentrations of sTNFα for 72 h compared to wild-type CGNs (WT). For figures a and b, LD50 TNFα values are indicated in Table 1. (c) Immunofluorescence experiments showing enhanced level of TNFR1 at the cell surface of PrPnull-1C11 and PrPnull-1C115-HT cells as well as PrP0/0 CGNs as compared to their corresponding PrPC expressing cells (CTRL, WT). Scale bar = 50 µm. (d) ELISA-based quantification experiments indicating reduced concentration of sTNFR1 in the culture medium of PrPnull-1C11/1C115-HT cells compared to PrPC expressing cells. *p < 0.01. (e) Western blots showing a stronger activation of caspase-3 in PrPnull-1C115-HT cells exposed to sTNFα (10 ng ml−1) for 120 min than in PrPC expressing cells. Antagonizing either ROCK activity with Y-27632 (100 µM for 1 h) or PDK1 activity with BX912 (1 µM for 1 h) in PrPC-depleted cells reduces toxic action of sTNFα. # p < 0.05 vs. PrPC-expressing cells exposed to sTNFα. ## p < 0.05 vs. PrPnull-cells treated with sTNFα. Data shown are the mean ± SEM from three experiments performed in triplicate.
