Figure 5.
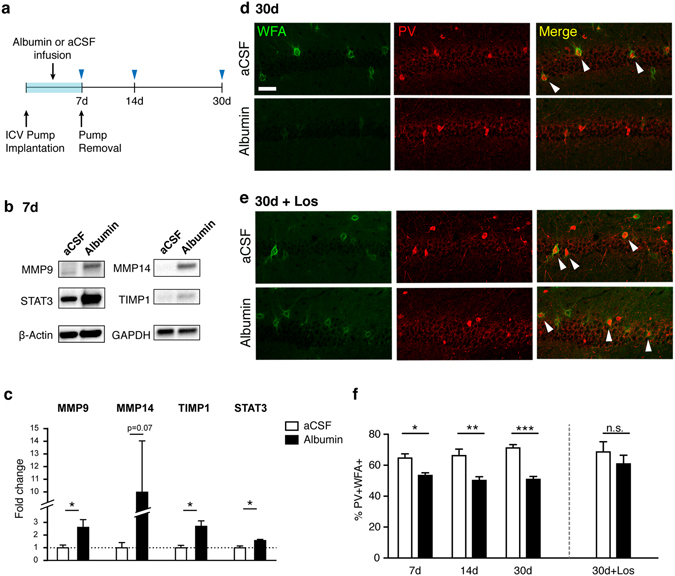
Albumin induced the degradation of perineuronal nets around PV(+) interneurons and losartan attenuated the effect of albumin. (a) Experimental design. Intracerebroventricular (ICV) osmotic pumps containing albumin (0.4 mM) or aCSF were implanted in rats and mice and removed after 7 days. (b,c) Molecules involved in ECM remodeling including MMP9, TIMP1, and STAT3 were significantly increased in dissected rat hippocampi following albumin infusion for 7 days. Uncropped blot images are available in the Supplementary Fig. S4. Each group has four biological replicates. Unpaired student t- test. *p < 0.05, two-tailed. (d) Representative confocal images showing PNNs (WFA) and PV(+) cells in the mouse hippocampal CA1 region at 30 days post implantation. (e) A separate set of animals was infused with albumin + losartan (10μM) or aCSF + losartan. Scale bar = 50 μm. (f) Albumin exposure decreased the association of PNNs with PV(+) interneurons (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Two-way ANOVA, post-hoc Sidak’s test, two tailed). Co-administration of losartan attenuated the effect of albumin (p > 0.05, Mann-Whitney test, two-tailed). n.s., not significant. Each condition has three or four biological replicates (n = 3–4).
