Figure 1.
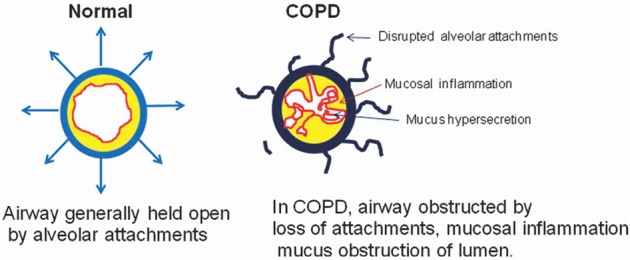
Air flow in Normal vs. COPD. The airway in normal condition is distended by alveolar attachments at the time of expiration. But in COPD these alveolar attachments are mainly disrupted due to emphysema, therefore contributing to airway closure during expiration, and hyperinflation due to air trap in the alveoli. Inflammation, fibrosis and mucus secretions further obstructed and distorted the peripheral airways and consequently create the poor mucociliary clearance (Barnes, 2004).
