FIGURE 1.
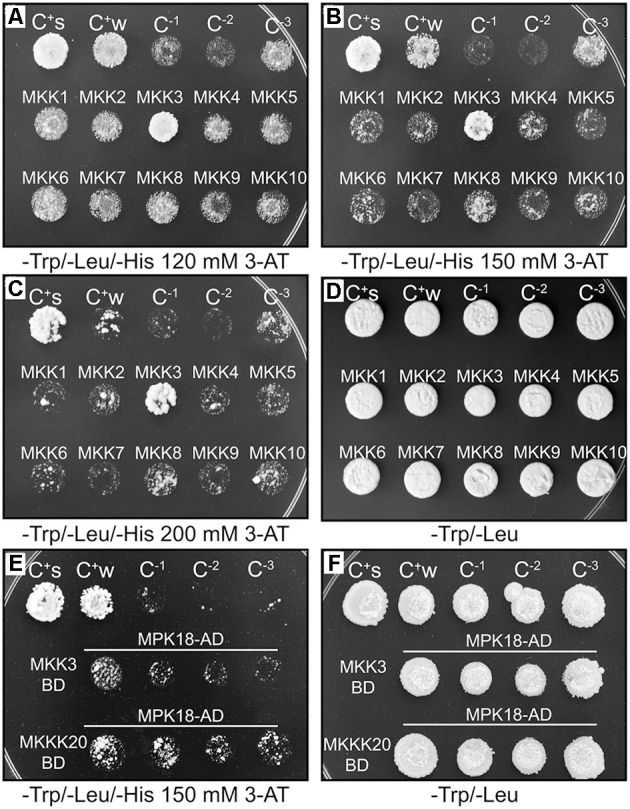
MKKK20/AtMKKs and MKK3/MPK18 yeast two-hybrid interactions. (A–D) MKKK20/AtMKKs interaction screen. MKKK20 interacts strongly with MKK3. All kinases were cloned and sequence-verified prior to their transfer into GatewayTM yeast two-hybrid bait and prey vectors (pDEST32 and pDEST22 from InvitrogenTM). The clones, MKKK20 (in pDEST32 vector) as GAL4 DNA-binding domain (DBD) and AtMKKs (in pDEST22 vector) as GAL4-activating domain (AD), were introduced pairwise into the yeast strain MaV203. Interaction strength for HIS3 and URA3 activation assays was scored visually by comparing to the controls. C+s: pEXPTM32/Krev1/pEXPTM22/RalGDS-wt as strong positive interaction control. C+w: pEXPTM32/Krev1/pEXPTM22/RalGDS-m1 as a weak positive interaction control. C-1: pEXPTM32/Krev1 pEXPTM22/RalGDS-m2 as a negative interaction control. C-2: pDESTTM32/pDESTTM22 as a negative activation control. C-3: pDESTTMMKKK20/pDESTTM22 as a negative activation control. (E,F). MKKK20 and MKK3 interaction with MPK18. MKK3 cloned as DBD and MPK18 as AD. The same controls were used as above except C-2 served as a negative activation control for MKK3 and C-2 as a negative activation control for MPK18.
