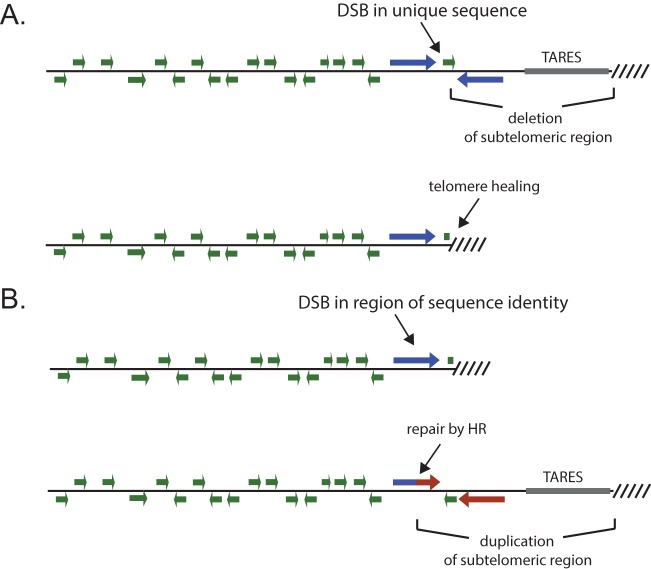
FIG 6 .
Model for the contribution of both telomere healing and homologous recombination in maintaining chromosome end stability in P. falciparum. (A) The occurrence of a DSB at a site of unique sequence within a subtelomeric region is stabilized by telomere healing. This results in a substantial deletion of the subtelomeric domain, including members of multicopy gene families and TAREs. (B) A subsequent DSB within a region that shares sequence identity with subtelomeric regions from other chromosomes can be repaired by HR, leading to reestablishment of the normal subtelomeric structure, including a full complement of multicopy genes and TAREs. Repair by HR can also result in chimeric genes, thereby contributing to the generation of diversity within the multicopy gene families.