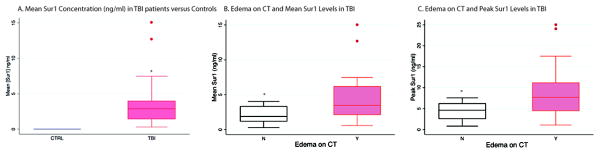
Figure 1.
A) Sur1 levels differed between patients with sTBI versus controls (p<0.001). The plot depicts the median (2.89 ng/ml) and inter-quartile range (1.32–3.97 ng/ml) of Sur1 in sTBI compared to the undetectable levels in controls. B) The difference in both mean (p=0.023) and peak (C, p=0.019) Sur1 levels between patients with and without edema on acute CT was statistically significant with higher levels noted in patients who had evidence of edema on acute CT. A higher presenting GCS score tended to decrease the odds of edema on acute CT (OR=0.59 95% CI 0.34–1.00, p=0.055, not shown).