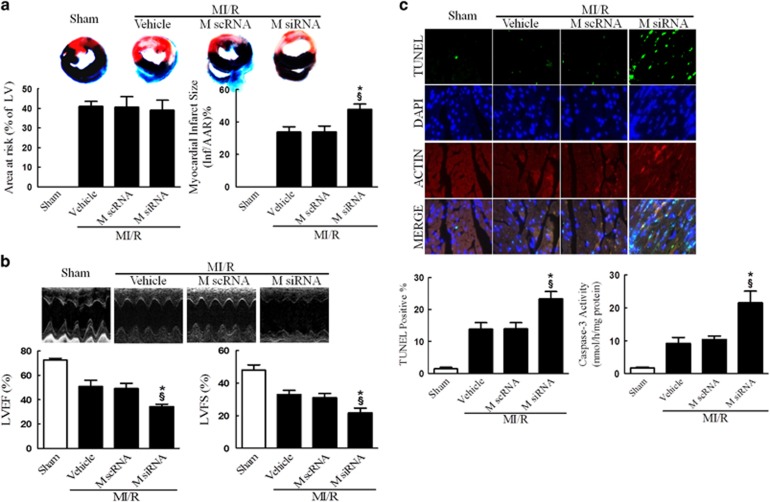
Figure 2.
MICU1 deficiency worsened MI/R injury. (a) Myocardial infarct size was assessed by Evans blue/TTC double staining. The upper panel showed heart sections obtained from mice at 24 h after MI/R injury. Evans blue-stained areas (black) indicated non-ischemic/reperfused area; TTC-stained areas (red staining) indicated ischemic but viable tissue; Evans blue/TTC-staining-negative areas indicated infarct myocardium. The lower panels showed summary of area at risk (AAR) per left ventricle (LV) and infarct area (Inf) per AAR. (b) Cardiac function was assessed by echocardiography in mice 24 h after MI/R injury. Representative M-mode images were shown in the upper panel. Left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) and fractional shortening (LVFS) were showed in the lower panels. (c) Myocardial apoptosis was determined by TUNEL staining in the upper panel. TUNEL staining (green) indicates apoptotic nuclei; DAPI counterstaining (blue) indicates total nuclei. TUNEL-positive nuclei were expressed as a percentage of the total number of nuclei, automatically counted and calculated by Image-Pro Plus software in the left of lower panel. Myocardial apoptosis was determined by caspase-3 activity assay in the right of lower panel. M scRNA, scrambled siRNA used as control; M siRNA, MICU1-specific siRNA. Presented values are means±S.E.M. N=6–8/group. *P<0.05 versus vehicle of MI/R; §P<0.05 versus M scRNA of MI/R