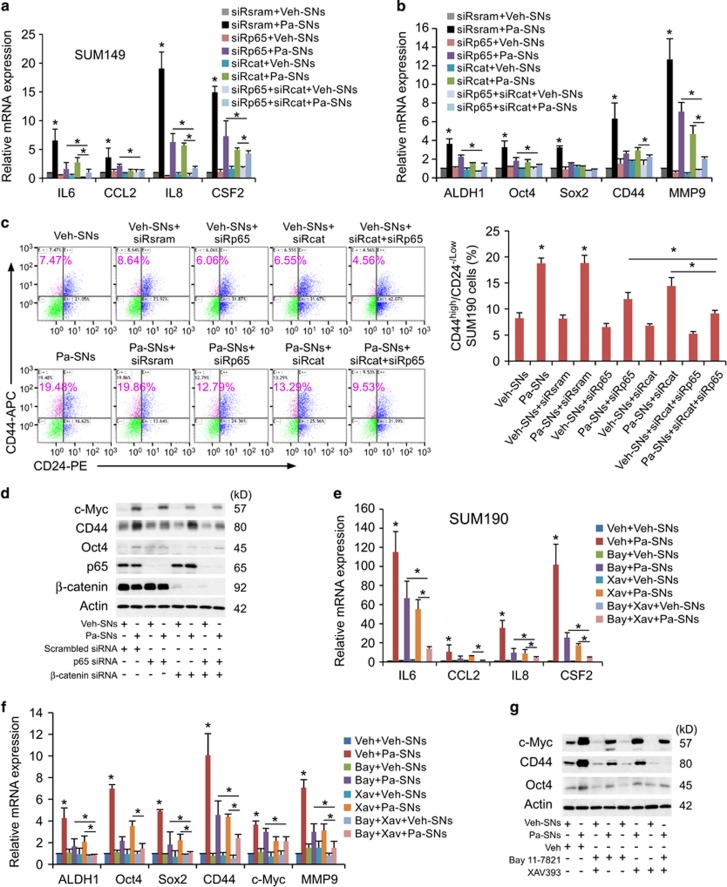
Figure 3.
Activation of Wnt/β -catenin and NF-κB pathways by the factors produced by breast cancer cells enhances the production of inflammatory cytokines from the same cell line, forming a forward-feedback loop to further promote CSC enrichment. (a-d). Knockdown of NF-κB (p65) and/or β-catenin markedly abolishes the upregulated cytokine genes, stem cell-associated genes (a and b, qPCR), CD44high/CD24-/low subpopulation (c, flow cytometry) and stem cell-associated proteins (d, western blot) after exposure to the paclitaxel-derived supernatants generated by the same cell line. Western blot also showed an almost complete knockdown of NF-κB p65 and β-catenin expression after transfection of NF-κB p65 and β-catenin siRNA with β-actin as an internal loading control. SUM149 cells were transfected with siRNA oligos against NF-κB p65 (siRp65), β-catenin (siRcat) or non-targeting oligos (siRsram) for 24 h, and then treated with vehicle (Veh)- or paclitaxel (Pa)-derived supernatants (SNs) for 4 days, followed by qPCR, flow cytometric and western blot analyses. Data represent means±S.D., n=3; *P<0.05. (e-g) Similar results are obtained by using small molecule inhibitors. Inhibition of NF-κB and β-catenin pathways effectively diminishes the upregulated expression of cytokine genes and stem cell-related genes (e and f, qPCR), and stem cell-related proteins (g, western blot with β-actin as an internal loading control) induced by paclitaxel-derived supernatants (Pa-SNs). SUM190 cells were pretreated for 2 h alone or in combination with vehicle (Veh), Bay 11-7821 (Bay, 5 μM, a NF-κB inhibitor) and/or XAV939 (Xav, 10 μM, a Wnt/β-catenin inhibitor), followed by exposure to vehicle (Veh)- or paclitaxel (Pa)-derived supernatants (SNs) for 4 days in the presence or absence of the same vehicle or inhibitors. Data represent averages±S.D., n=3; *P<0.05. See also Supplementary Figures 4 and 5