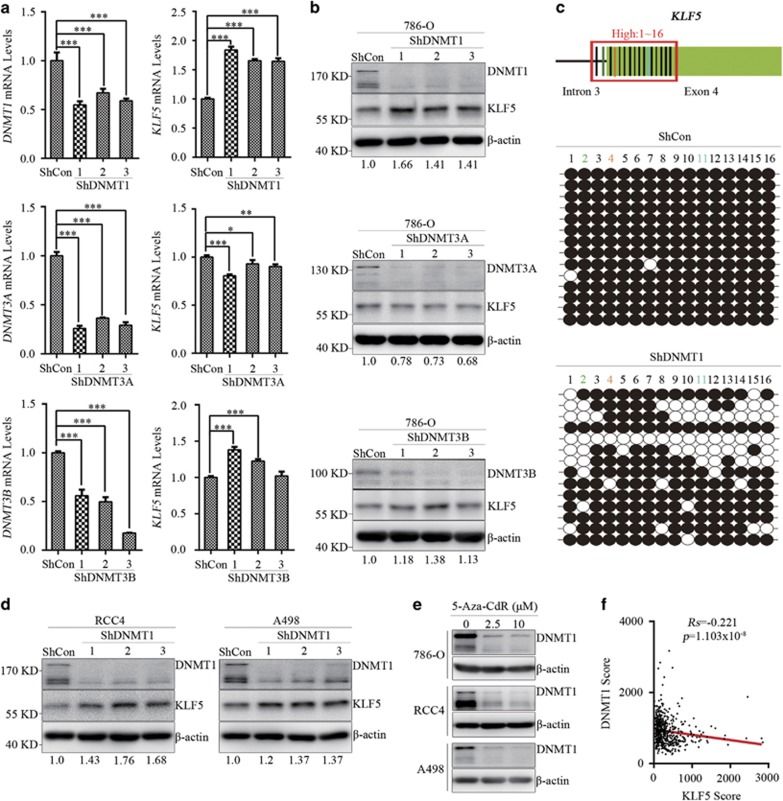
Figure 3.
Hypermethylation of KLF5 gene is mainly maintained by DNMT1. (a,b) 786-O cells were infected with ShDNMTs or ShControl (ShCon) lentivirus, then qPCR (a) and western blots (b) were applied to detect mRNA and protein levels of KLF5 and DNMTs. (c) Bisulfite sequencing (down) was applied to analyze the methylation levels of diagram-indicated loci (up) in high-methylated areas (1–16). Open circles (○), unmethylated cytosine; closed circles (•), methylated cytosine. (d) Western blots were utilized to detect expression of KLF5 in ShDNMT1 or ShCon-expressing RCC4 or A498 cells. Quantity One software was used to normalize KLF5 expression. Expression level of KLF5 was normalized to its internal control, and relative expression of KLF5 in ShDNMTs-expressed ccRCC cells were compared with that in ShCon-expressed cells. (e) Western blots for expression of DNMT1 in indicated ccRCC cell lines with or without 5-Aza-CdR treatment. (f) Scatter plots for the inverse correlation of KLF5 with DNMT1 expression in ccRCC patients (n=652) from online TumourProfile database. Spearman rank correlation test, Rs=Spearman rank correlation coefficient. All bar graphs are plotted as mean±S.D. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t-test