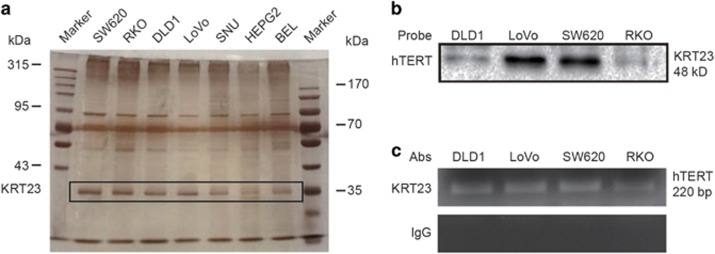
Figure 1.
KRT23 was identified and validated as a transcription factor of hTERT in CRC cells. (a) A streptavidin–biotin pulldown assay was performed to identify the specific proteins that bind to the hTERT promoter. Nuclear extracts prepared from human CRC cells (SW620, RKO, DLD1 and LoVo) and hepatoma carcinoma cells (SNU, HEPG2 and BEL) were incubated with a biotin-labeled hTERT promoter probe and streptavidin–agarose beads. The DNA–protein complexes were separated by SDS-PAGE, and the protein bands were visualized by silver staining. The protein bands (at ~35 kDa) were excised from the gel and identified by the mass spectrum analysis. We predicted that the candidate CRC-specific hTERT promoter-binding protein was KRT23. (b) Immunoblot assay for detecting KRT23 binding to the hTERT promoter probe. KRT23 protein in the DNA–protein complexes was detected by western blot assay using an anti-KRT23 antibody. (c) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (CHIP) assays were performed using the hTERT promoter from human CRC cells (SW620, RKO, DLD1 and LoVo). PCR products were separated on 1% agarose gels. Normal immunoglobulin G (IgG) was the negative control for the KRT23 antibody