Fig. 3.
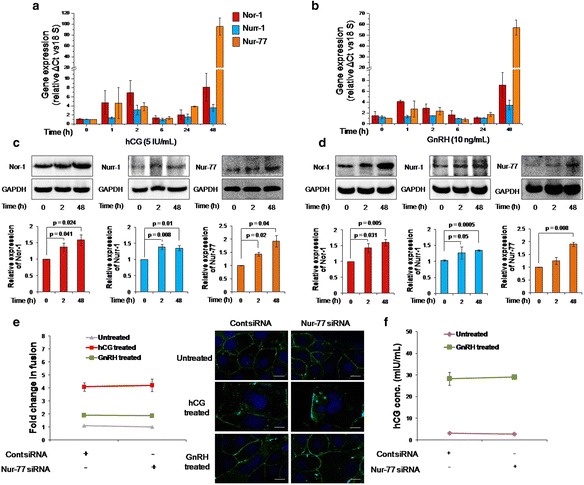
Effect of Nur-77 knockdown on hCG- and GnRH-mediated cell fusion and hCG secretion. BeWo cells were treated with either hCG (5 IU/ml) or GnRH (10 ng) for various times. Subsequently, total RNA and cell lysates were isolated and processed for qRT-PCR and Western blotting, respectively, to analyze the transcript and protein levels of Nor-1, Nurr-1 and Nur-77. a and b – qRT-PCR analysis of Nor-1, Nurr-1 and Nur-77 in the form of bar graphs of BeWo cells treated with hCG and GnRH, respectively. Relative expression was normalized with 18S rRNA. Data are expressed as means ± s.e.m. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. c and d – Protein expression profiles of Nor-1, Nurr-1 and Nur-77 in BeWo cells after treatment with hCG and GnRH, respectively, with GAPDH used as an internal control. Values are expressed as means ± s.e.m. of the band intensity of three independent experiments. Representative blots for the same experiment are appended with the graphs. BeWo cells transfected with either Nur-77 siRNA or control siRNA were treated with either hCG (5 IU/ml) or GnRH (10 ng/ml). The fold change in fusion was estimated after 48 h using desmoplakin I + II staining and hCG secretion was analyzed in GnRH treated cells via ELISA. e – The effect of hCG and GnRH treatment in the control and Nur-77-silenced BeWo cells on fusion at 48 h. The data are expressed as means ± s.e.m. of three independent experiments. Representative images of desmoplakin I + II staining in green and DAPI in blue are appended alongside. The scale bar is 20 μm. f – hCG secreted by control and Nur-77-silenced BeWo cells in response to GnRH treatment at 48 h. Data are represented as means ± s.e.m. of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. p ≤ 0.05 is considered statistically significant
