FIGURE 2.
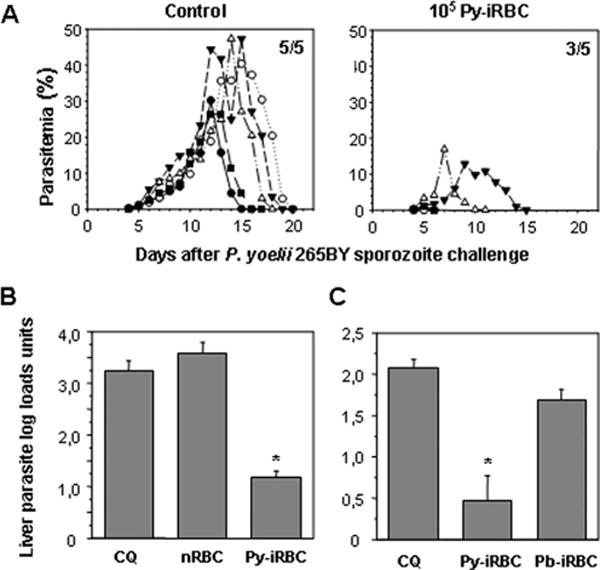
Immunization with iRBC under chloroquine cover induces protective immunity against a sporozoite challenge. A, Blood stage parasitemia in BALB/c mice challenged with 4000 homologous sporozoites 25 days after immunization with 105 Py-iRBC or 105 normal RBC under 10 days chloroquine cover. Parasitemia was monitored in each animal by microscopic examination of Giemsa-stained blood smears. Only points at which parasitemia was patent were plotted. A different symbol is assigned to each animal in the group. The number of mice with patent parasitemia relative to the total number of mice in the group is shown (top right corner). B C, Liver parasite loads in immunized mice challenged with sporozoites. Groups of BALB/c mice were either immunized with matching numbers of normal RBC (nRBC), with 106 Py-iRBC (B) or 106 P. berghei ANKA iRBC (Pb-iRBC) (C) on the day when a 10-day chloroquine treatment was initiated, or treated with chloroquine alone (CQ). Mice were then challenged with 35,000 P. yoelii 265BY sporozoites 25 days or more after immunization, liver parasite development was quantified. Results were expressed as mean liver parasite load log units ± SEM of n = 5 mice. Reduction of parasite load was more than 95% when the arithmetic values were used for calculation. *, p < 0.05, vs control mice using ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test.
