Figure 2.
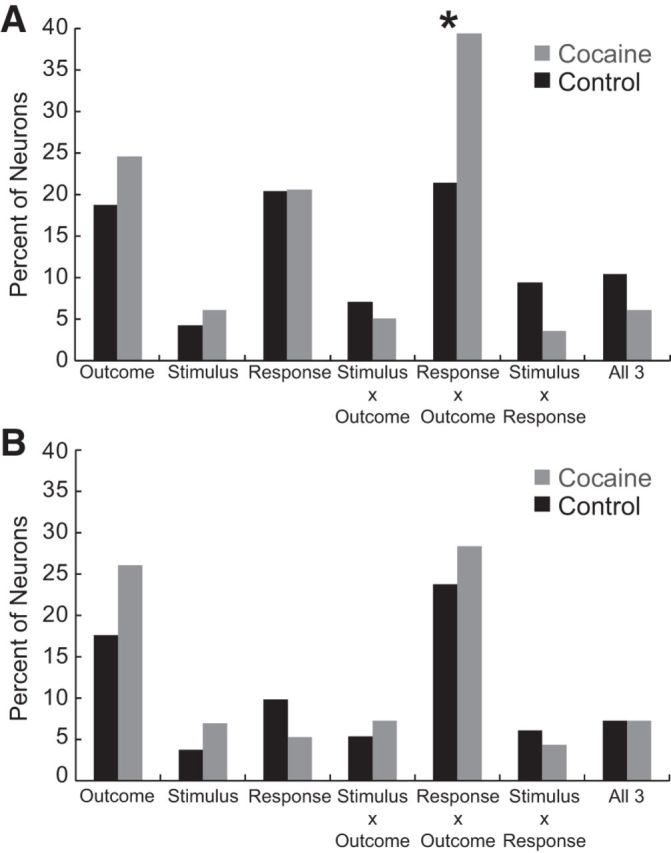
Percentage of increasing-type neurons (A) (control, n = 126, 22%; cocaine, n = 100, 27%) and decreasing-type neurons (B) (control, n = 262, 47%; cocaine, n = 123, 34%) with activity that was modulated significantly by outcome, stimulus, response, and interactions between these three factors in the ANOVA. *p < 0.05, χ2 test.
