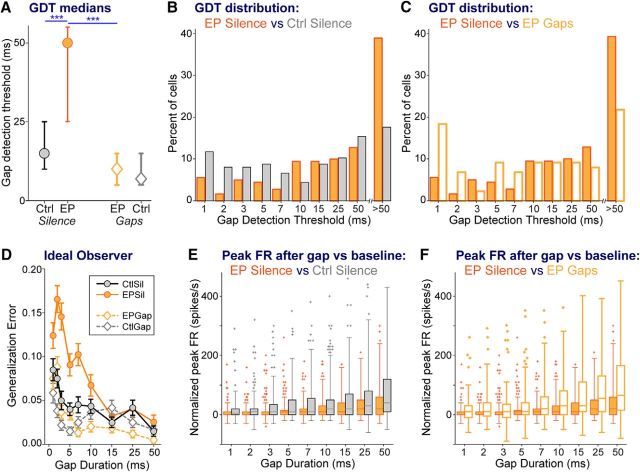
Figure 4.
Cortical GDTs are worsened by early hearing loss, and remediated to control levels by stimulus exposure. A, Median GDTs (with 95% confidence intervals). B, For silence-exposed animals, distribution of GDTs of groups with and without earplugs, showing that the difference in median GDT reflects earplugged animals having fewer cells with low GDTs and more cells with high GDTs. C, For earplugged animals, distribution of GDTs of groups with and without stimulus exposure, showing that the difference in median GDT reflects remediated animals having more cells with low GDTs and fewer cells with high GDTs. D, The function generated by an ideal observer model plots the error made by the model for correctly detecting gaps of specific durations, based on the firing rate in the window immediately following the gap. The ideal observer model predicts reduced sensitivity with increasing gap durations. Furthermore, for short gap durations of <15 ms, the ideal observer model reveals poorer performance for the EPSil neurons compared with the other three groups. Error bars are SEM based on 100 runs of the model. E, F, Across gap durations, boxplots of peak firing rates (FRs) within the time window following each gap, allowing comparisons between (E) CtSil and EPSil groups and (F) EPSil and EPGap groups. These peak FRs are the values used to generate the analyses in A–D. Planned comparisons: ***p < 0.0002.