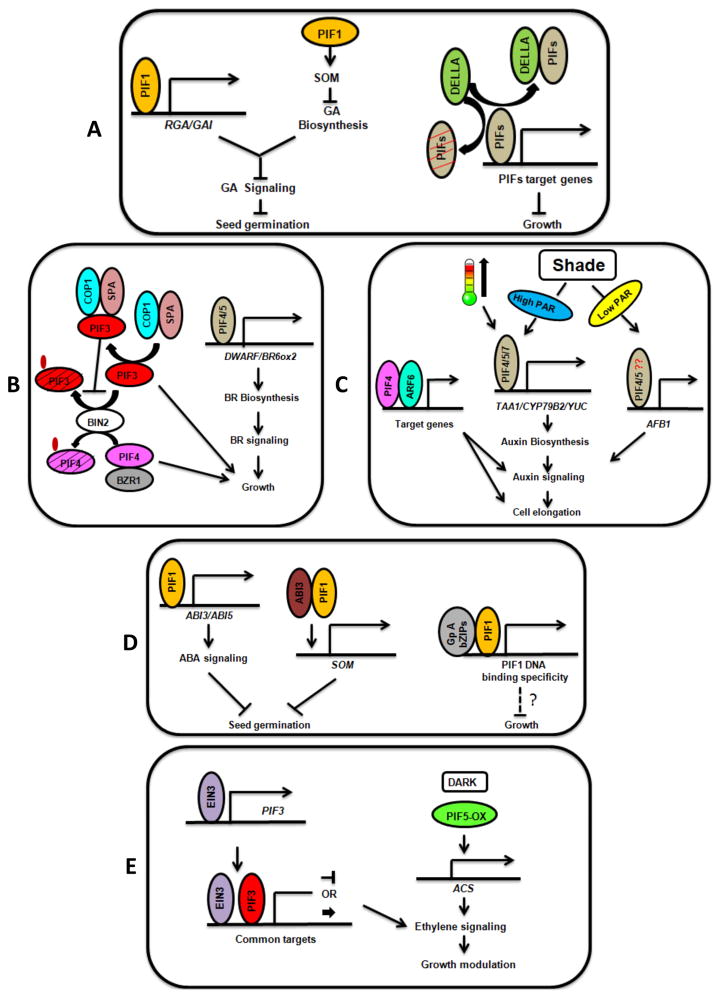
Figure 3.
PIFs integrate light and hormone signaling pathways to modulate growth in Arabidopsis.
(A, left) PIF1 has an exclusive role in regulating seed germination by directly activating RGA and GAI expression that inhibit GA signaling. PIF1 also inhibits GA biosynthesis indirectly by activating SOM expression, resulting in inhibition of seed germination in the dark. Light-induced degradation of PIF1 promotes seed germination. (Right) PIFs physically interact with DELLA proteins and this interaction results in inhibition of DNA binding activities of PIFs. DELLA proteins also induce degradation of PIFs in darkness and inhibit subsequent growth. (B, left) PIF4 interacts with BZR1 and regulates growth in response to BR and light signal. BIN2 phosphorylates PIF3 and PIF4 independent of light and promotes their degradation in darkness. However, COP1/SPA1 interact with PIF3 and prevent BIN2-mediated phosphorylation and degradation in the dark. (Right) PIF4 and PIF5 directly activate BR biosynthetic pathway genes to promote growth. (C, left) PIF4 forms a complex with ARF6 and promotes growth in response to light and auxin signaling. (Middle) In response to high ambient temperature and shade conditions, PIF4/PIF5/PIF7 promote auxin biosynthesis to promote cell elongation. (Right) PIF4/PIF5 and possibly other PIFs also activate the expression of auxin receptor AFB5 in response to low PAR shade conditions to promote auxin signaling and subsequent growth. (D, left) PIF1 directly activates the expression of the ABA signaling components (ABI3 and ABI5). PIF1 also interacts with ABI3 and the PIF1-ABI3 complex directly inhibits the expression of SOM, which in turn inhibits GA biosynthesis to suppress seed germination. (Right) PIF1 and possibly other PIFs directly interact with group A bZIP proteins (e.g., ABI5). This interaction regulates the DNA binding specificity and target gene selection of PIF1 and possibly other PIFs. (E, left) Ethylene signaling factor, EIN3 directly activates the expression of PIF3, which in turn binds to DNA along with EIN3 to regulate ethylene signaling as well as chlorophyll biosynthesis and growth. (Right) Overexpression of PIF5 activates the expression of ACC Synthase (ACS) genes, which results in increased ethylene biosynthesis and signaling to modulate growth.