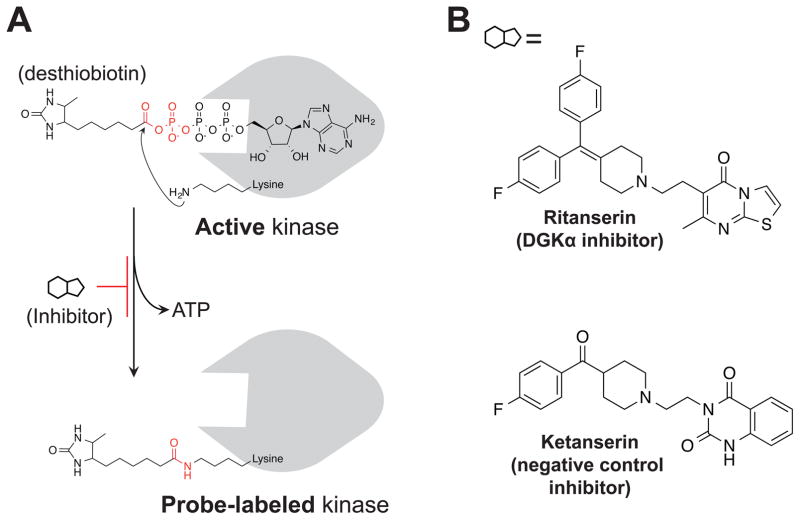
Figure 2. Activity-based probes and inhibitors for functional analysis of DGKs.
(A) Chemical structure and mechanism of ATP acyl phosphate probe labeling. The ATP binding group mediates interactions with lipid and protein kinases to place the reactive acyl phosphate group in proximity of lysines in the active site. The side chain amino group of lysine covalently reacts with probe, releasing ATP, and covalently attaches desthiobiotin to kinase through an amide bond. (B) The DGKα inhibitor ritanserin and matching negative control inhibitor ketanserin.