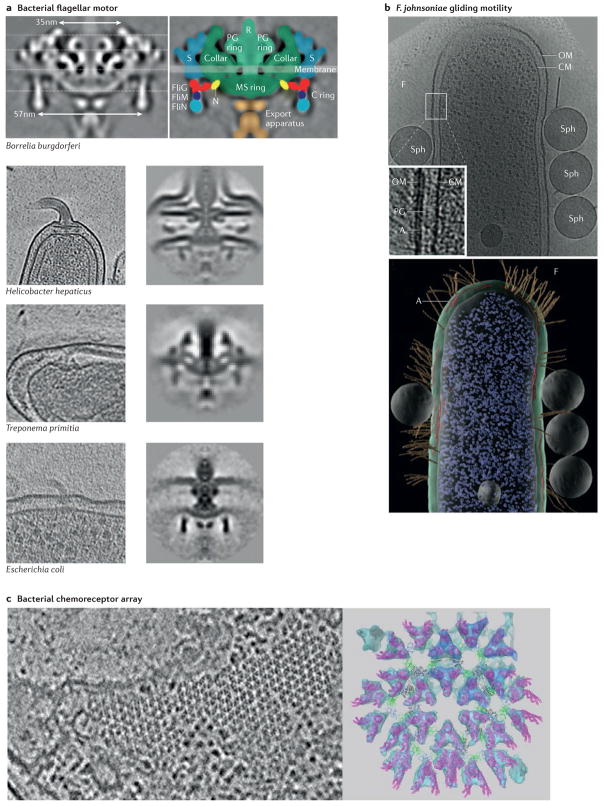
Figure 3. Motility and navigation.
a | Electron cryotomography (ECT) and subtomogram averaging have revealed the high-resolution structure of the bacterial flagellar motor (top panel), and imaging different species has uncovered species-specific structural adaptations (bottom panels). Top left and bottom right columns show subtomogram averages; bottom left column shows slices through tomographic reconstructions. b | ECT has also helped to identify the different motility mechanisms used by other bacteria, such as the filament-mediated gliding motility of Flavobacterium johnsoniae. The top panel shows a slice through a tomographic reconstruction of the bacterium, and the bottom panel a 3D segmentation. The electron-dense patches underlying filaments (A) and the latex spheres used to identify regions of motility (Sph) are indicated. c | High-resolution ECT and subtomogram averaging revealed the hexagonal lattice structure of the chemoreceptor arrays that bacteria and archaea use to direct motility. The image on the left is a slice through a tomographic reconstruction of an Escherichia coli cell, and the image on the right is a top view of a pseudo-atomic model of crystal structures docked into a subtomogram average (shown in cyan). Chemoreceptors are shown in magenta, the coupling protein CheW is shown in green and two domains of the kinase CheA are shown in black and blue. CM, cytoplasmic membrane; F, filament; MS ring, membrane and supramembrane ring; N, amino terminus; OM, outer membrane; PG, peptidoglycan; R, rod; S, stator. Top panel of part a is from J. Bacteriol., 2009, 191, 5026–5036 http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JB.00340-09 and reproduced with permission from American Society for Microbiology. Bottom panel of part a is modified with permission from REF. 66, EMBO press. Part b is from J. Bacteriol., 2007, 189, 7503–7506 http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JB.00957-07 and reproduced with permission from American Society for Microbiology. Left panel of part c is modified with permission from REF. 99, Wiley. The right panel of part c is modified with permission from REF. 97, National Academy of Sciences.