Fig. 3.
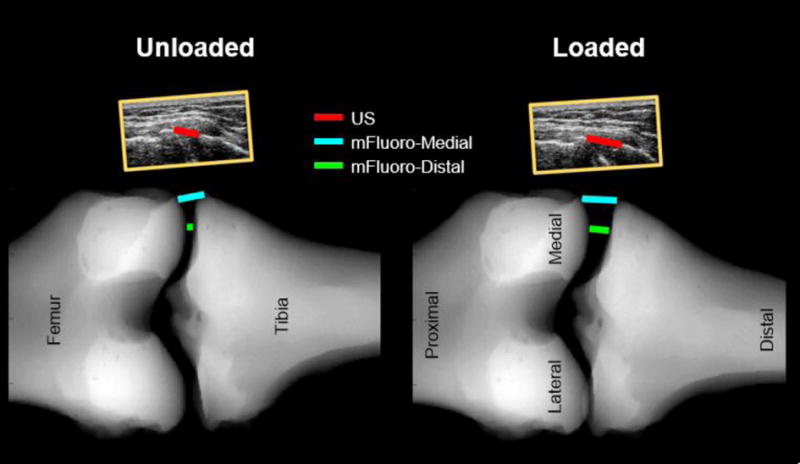
Comparison of the measurement locations of the US, mFluoro-Medial and mFluoro-Distal approaches. The ultrasound images can be seen (to scale) above the mFluoro images. The US gap width was estimated by manually selecting the most medial point on the femur and tibia. mFluoro gap widths were estimated automatically from the mFluoro images. For the mFluoro-Medial method, the most medial aspects of the femur and tibia were selected. For the mFluoro-Distal approach the most distal aspect of the femur was identified and then the corresponding point on the tibia plateau was found by projecting a line parallel to the axis of the tibia and finding the intersection between this line and the edge of the tibial plateau.
